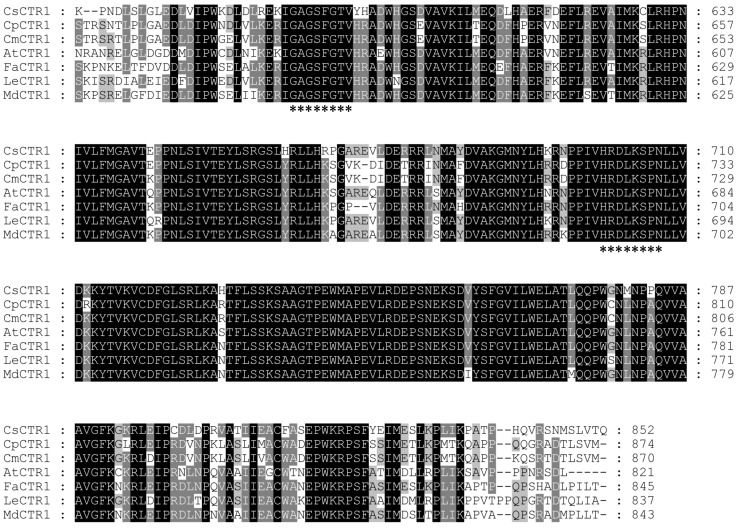
Figure 2.
Multiple amino acid sequence alignments of the C-terminal Ser/Thr kinase domain in the CTR1-like proteins of several plant species. Seven genes from Malus × domestica (MdCTR1, ABI58290), Solanum lycopersicum (LeCTR1, AAL87456), Cucumis melo (CmCTR1, ADV92636), Cucurbita pepo (CpCTR1, ADB55631), Arabidopsis thaliana (AtCTR1, CAB82938), Fragaria × ananassa (FaCTR1, AFI38955) and Cucumis sativus (CsCTR1, AEZ53932) were used for multiple sequence alignment. Amino acids with identities of over 75% are shaded in black; whereas, those with identities ranging between 50% and 75% are shaded in gray. The ATP binding signature (GxGxxGxV) and the protein kinase active site consensus sequence (HRDLKxxN) are indicated by asterisk. Numbers for amino acids are indicated on the right.