Figure 3.
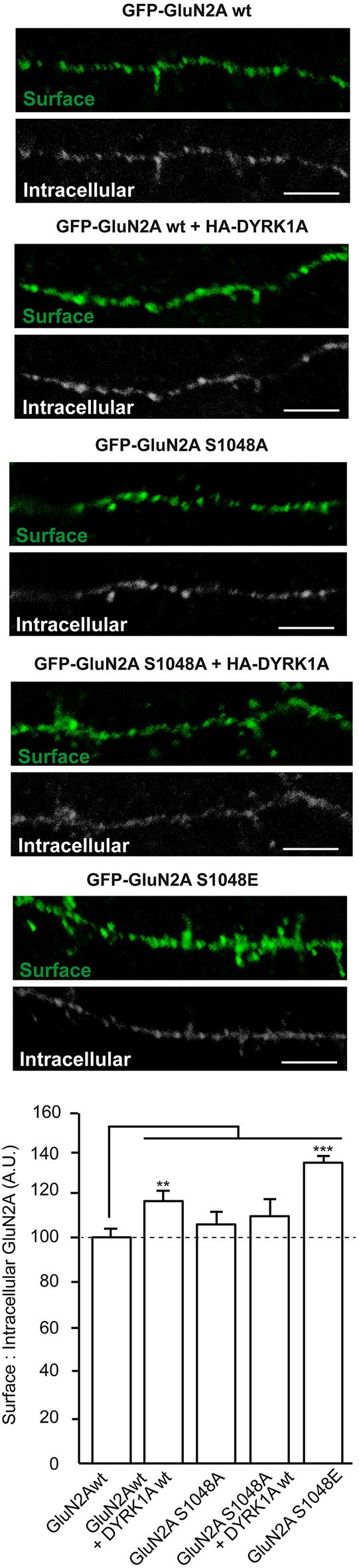
Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A mediated phosphorylation of GluN2A at S1048 increases its surface expression in primary cortical neurons. Primary cultures of mouse embryo cortices were transiently transfected with GFP-GluN2A (wt, wild-type; S1048A, phospho-deficient mutant; S1048E, phospho-mimetic mutant) on day in vitro 8 (DIV8), in the presence or absence of heterologous HA-DYRK1A. The effect of DYRK1A on the surface:intracellular ratio of GluN1/GluN2A in primary mouse cortical neurons was evaluated by immunofluorescence. Prior to permeabilization, anti-GFP/Alexa488 was used to detect the surface chimeric receptors (represented in green), whereas intracellular GFP-GluN2A receptors were visualized after permeabilizing the cells, using an anti-GFP/Alexa555 antibody. Scale bar = 5 µm. The histogram represents the mean ± SEM GluN2A surface expression normalized to the intracellular GFP-GluN2A signal (n = 31–52 dendrites from, at least, three independent experiments per condition, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ANOVA).
