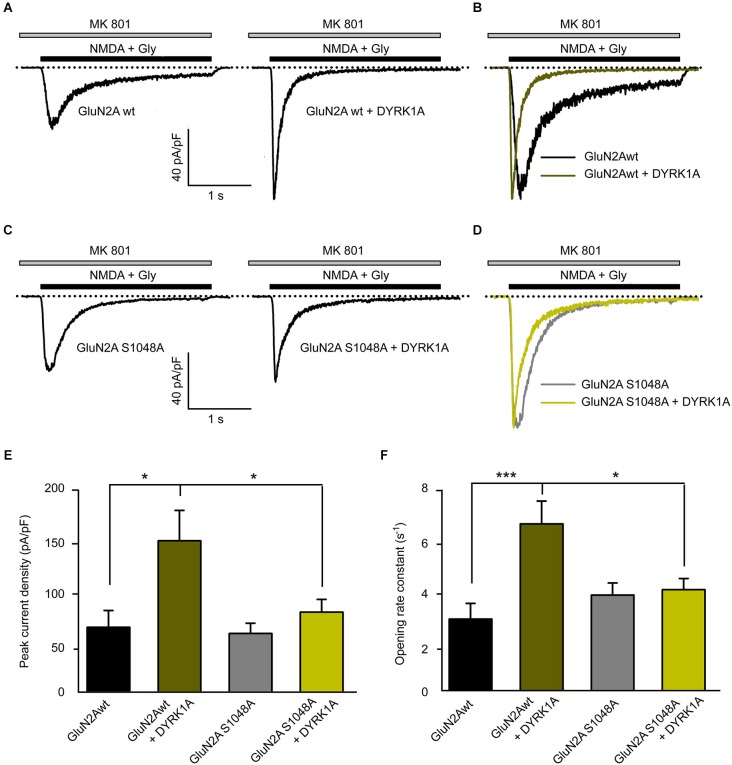
Figure 5.
Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A increases the NMDA-elicited current amplitude and opening rate. (A–D) Representative NMDA-elicited currents recorded from HEK-293T cells expressing HA-GluN1/HA-GluN2A receptors (panels A,B, wild-type GluN2A; panels C,D, GluN2AS1048A phospho-deficient mutant) in the presence (right) or absence (left) of GFP-DYRK1A. Whole-cell currents were elicited by perfusion of 1 mM NMDA with 50 µM glycine, in the continued presence of the open-channel blocker MK-801 (5 µM). (B,D) NMDA-evoked currents shown in panels (A) and (C) normalized to the same peak amplitude. (E) Average peak NMDA-evoked current density in cells transfected with NMDARs (GluN2Awt or GluN2AS1048A) in the presence or absence of DYRK1A (*p < 0.05, ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). (F) Average opening rate of heterologously expressed NMDARs (GluN2Awt or GluN2AS1048A) in the presence or absence of DYRK1A (***p < 0.001 and *p < 0.05, ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post hoc test).