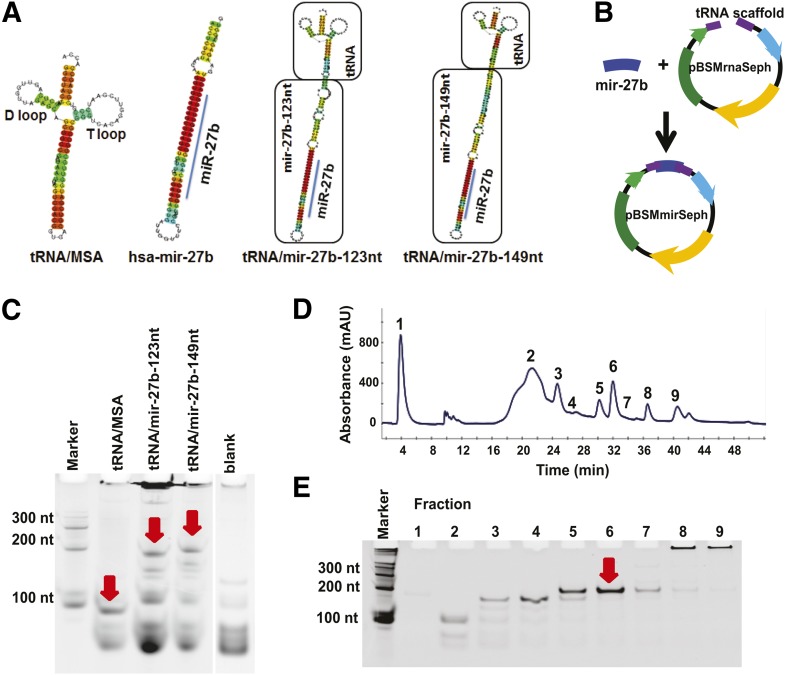
Fig. 1.
Design and production of recombinant tRNA-fusion pre-miR-27b agents. (A) Secondary structures of tRNA/MSA, hsa-mir-27b, and chimeric tRNA/mir-27b-123nt and tRNA/mir-149nt were predicted by CentroidFold. Consistent results were obtained using Centroidhomfold and RNAstructure. (B) The target hsa-mir-27b inserts encoding mir-27b-123nt and mir-27b-149nt were ligated into the pBSMrnaSeph vector linearized by endonucleases SalI and AatII to produce the recombinant pre-miRNA expression plasmids (pBSMmirSeph). (C) The tRNA/mir-27b-123nt and -149nt chimeras were successfully expressed in E. coli. The arrows indicate the recombinant ncRNA bands at expected sizes. Total RNAs (1 μg per lane) were analyzed by denaturing polyacrylamide (8%) gel electrophoresis. Untreated bacteria (blank) served as control. (D) FPLC traces during the purification of chimeric tRNA/mir-27b-149nt. Total RNAs were separated using anion-exchange FPLC and monitored at 260 nm. (E) Denaturing polyacrylamide (8%) gel electrophoresis indicated that fraction #6 consisted of high-purity (>95%) recombinant tRNA/mir-27b-149nt. Similar results were obtained for tRNA/mir-27b-123nt (data not shown).