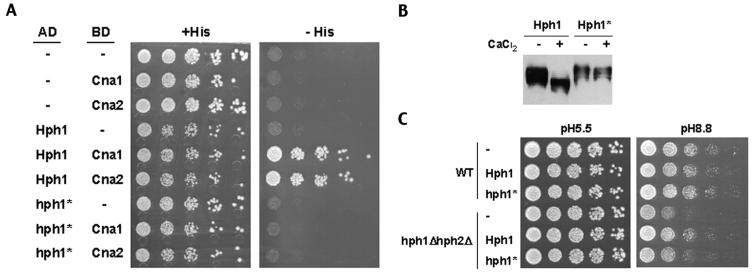
FIG. 5.
Hph1p lacking the motif PVIAVN does not bind Cna1p or Cna2p, is not dephosphorylated upon treatment with CaCl2, and only partially complements the growth defects of the hph1Δ hph2Δ mutant at high pH. (A) A yeast two-hybrid assay was set up with PJ69-4A cells expressing CNA1 (BJP2014) or CNA2 (pVH7) GAL4 binding domain fusions (BD) in combination with GAL4 activation domain fusions (AD) of wild-type HPH1 (pVH3) or HPH1-ΔPVIAVN (Hph1*) (pVH5), as indicated. Cells were plated on medium containing (+His) and lacking (−His) histidine and incubated for 3 days at 30°C. (B) Wild-type (WT, YPH499) cells expressing GFP-Hph1p (pVH1) or GFP-Hph1-ΔPVIAVNp (GFP-Hph1*) (pVH12) were grown to log phase and then either mock treated or treated with 200 mM CaCl2 for 10 min. Samples were then frozen in liquid N2, extracts were prepared, and SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting with an anti-GFP antibody was performed (see Materials and Methods). (C) Wild-type (WT, BY4741) and hph1Δ hph2Δ (VHY60) cells were transformed with either empty vector (−) (pRS315) or plasmids to express endogenous levels of wild-type Hph1p (pVH8) or Hph1-ΔPVIAVN (Hph1*) (pVH9). Cultures were grown in selective synthetic medium to the stationary phase, diluted as described for Fig. 3, plated on YPD at pH 5.5 (50 mM MES) and YPD at pH 8.8 (50 mM Tris), and incubated at room temperature for 3 and 4 days, respectively.