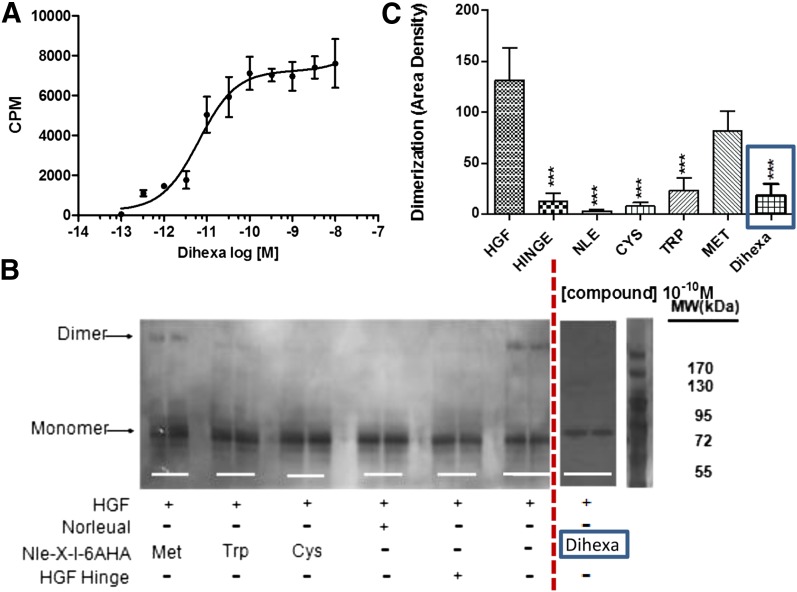
Fig. 1.
Binding of the HGF mimetic dihexa to HGF and its impact on HGF dimerization. (A) Dihexa binds saturably and with high affinity to HGF. The binding of [3H]dihexa to HGF was assessed using a soluble binding assay. Saturation isotherms were developed for the interaction of [3H]dihexa with HGF. Human HGF (1.25 ng) in 250 μl of PBS were incubated with multiple concentrations of [3H]dihexa ranging from 10–13 M to 10–8 for 40 minutes at 37°C. The incubates were then spun through Bio-Gel P6 spin columns (400 μl packed volume) for 1 minute to separate free and bound [3H]dihexa and the eluent collected and counted. Graph is a composite of three experiments run in quadruplicate. N = 3, mean ± S.E.M. (Kd = 6.52 × 10–11 M). (B) Dihexa blocks HGF dimerization. HGF dimerization was assessed in the presence of various analogs including dihexa. Norleual, the Nle-X-6AHA (Cys, Met, Trp) analogs, and HGF Hinge have been shown to be HGF antagonists (Yamamoto et al., 2010; Kawas et al., 2011, 2012). Dimerization was carried out for 30 minutes in the presence of heparin. Samples where crosslinked with bissulfosuccinimidyl suberate (BS3) and separated by native PAGE. Bands were visualized by silver staining and (C) quantitated by densitometry. (N = 6; ***P < .001.) [Some of the data in (B) was previously published (Kawas et al., 2012) and is being presented for comparison purposes.] CPM, counts per minute.