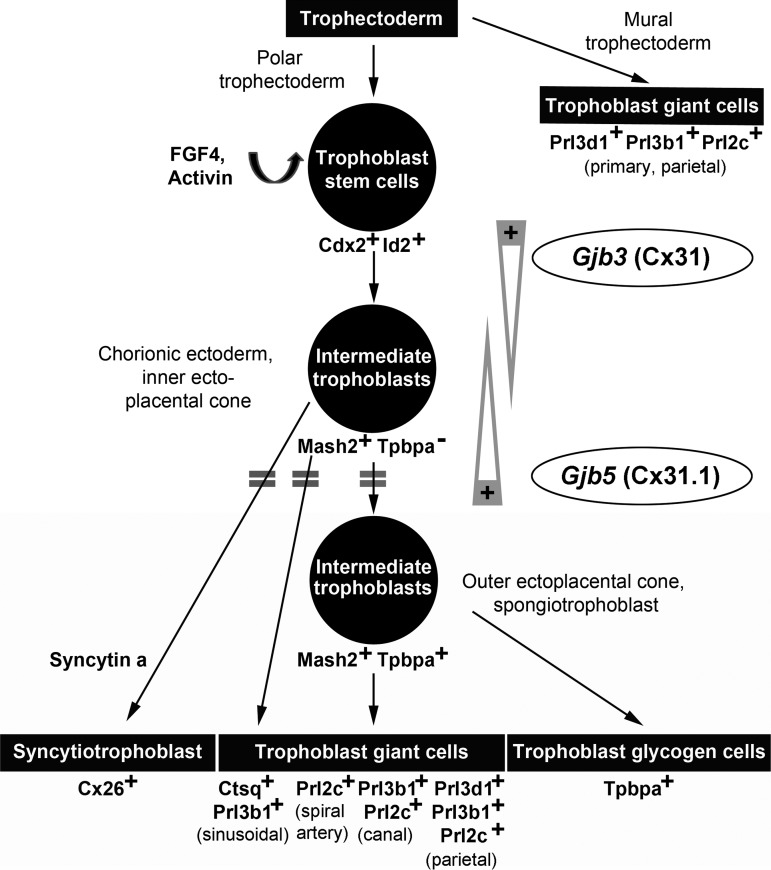
FIG. 7.
Model for the role of Cx31 and Cx31.1 in trophoblast lineage differentiation and placental development. The scheme integrates the phenotypes of the Cx31 and Cx31.1 knockout mice into the current spatio-temporal model of murine trophoblast lineage differentiation. Upon differentiation, trophoblast cells pass through a proliferative, Ascl2/Mash2-positive state within the chorionic ectoderm and ectoplacental cone before terminal differentiation into the placental subpopulations. The delayed induction of marker genes (indicated by double bars) in Cx31.1-deficient trophoblasts suggests a coordinated role for Cx31 and Cx31.1 in regulation transition through the Ascl2/Mash2-positive state. Cx31 is required to maintain the stem cells state and preserve the intermediate Ascl2/Mash2-positive state during trophoblast differentiation, whereas Cx31.1 is required to push cells into terminal differentiation, indicating the balancing, opposed function of both connexins (gray arrows) during murine placental development.