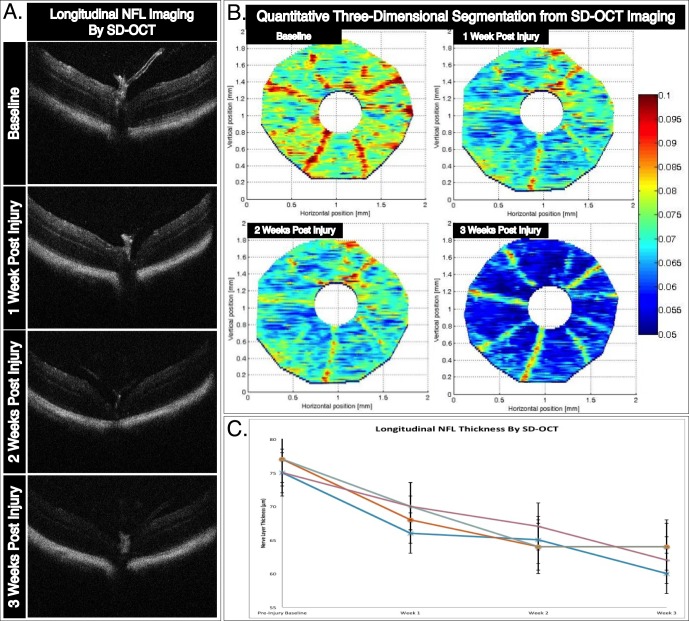
Figure 4.
In vivo longitudinal and topographic assessment of NFL thickness as a surrogate marker for RGC survival. (A) Representative B-scan cross-sectional images tracking longitudinal thinning of the NFL layer following ONC injury. The B-scan images were taken directly over the optic nerve head at baseline, and 1, 2, and 3 weeks after injury. (B) Three-dimensional retinal thickness maps obtained through manual segmentation of SD-OCT imaging show progressive pathophysiological changes to the mouse retina following ONC injury. In this representative example, a single mouse retina is tracked over three weeks following injury. (C) Average NFL thickness for each manually segmented retina decreased in thickness following ONC. Topographic three-dimensional retina thickness maps were obtained by segmentation of NFL thickness of over 100 B-scans per retina. Error bars: standard deviation.