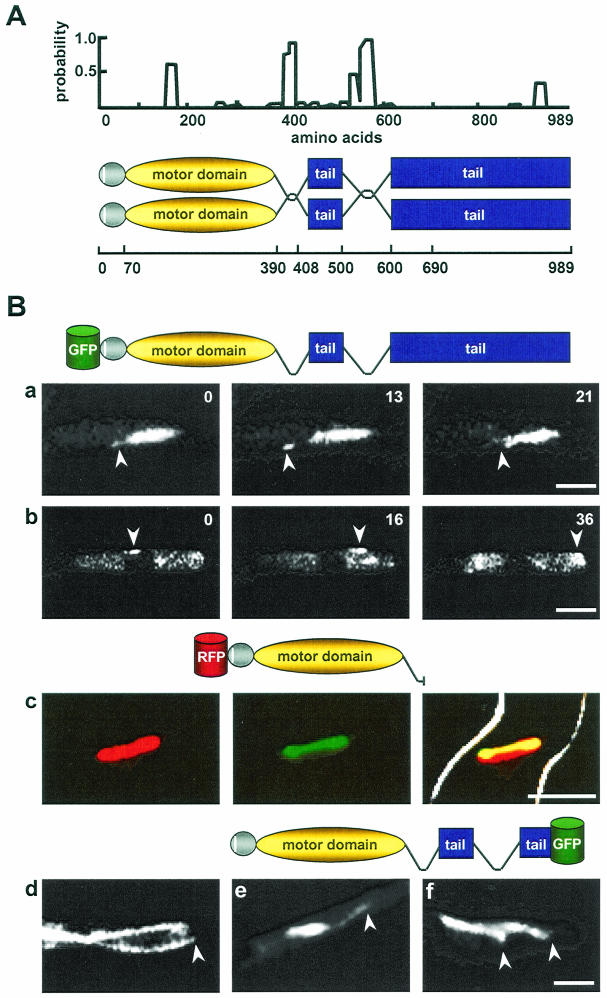
FIG. 9.
Localization of GFP-KipB fusion proteins. (A) Coiled-coil prediction (23) for KipB (window size 14). A significant coiled-coil probability was found for amino acids 390 to 408 and 500 to 600. The schematic drawing shows the domains of the KipB protein, including globular heads (gray), the amino-terminal motif of 18 amino acids (white), the coils (curved lines), and the tail domain (blue). The amino acid positions are represented on the line below. (B) Localization of different GFP-KipB fusion proteins. (a and b) Time-lapse analysis of full-length KipB protein tagged N-terminally with GFP (see the schematic drawings of the different constructs above each series of photos). For strain SPR96, the images show the localization of GFP-KipB onto spindle and astral MTs, with arrows pointing to the plus ends of the astral MTs (see Video S5 in the supplemental material) (a) and spots of GFP-KipB moving onto cytoplasmic MTs (see Video S6 in the supplemental material) (b). (c and d) Colocalization between a truncated version of mRFP1-KipB and the mitotic spindles (see Video S8 in the supplemental material) for strain SPR98. Left, mRFP1-KipB; middle, α-tubulin-GFP; right, merged images of the first two photos. (d) Localization to cytoplasmic MTs. The arrow points to the plus end of the MT in the hyphal tip. (e and f) C-terminal fusion of KipB with GFP (see Video S7 in the supplemental material) in strain SPR2. The images show the localization onto mitotic and astral (arrow) MTs (e) and cytoplasmic MTs (arrows) (f). Bar, 5 μm.