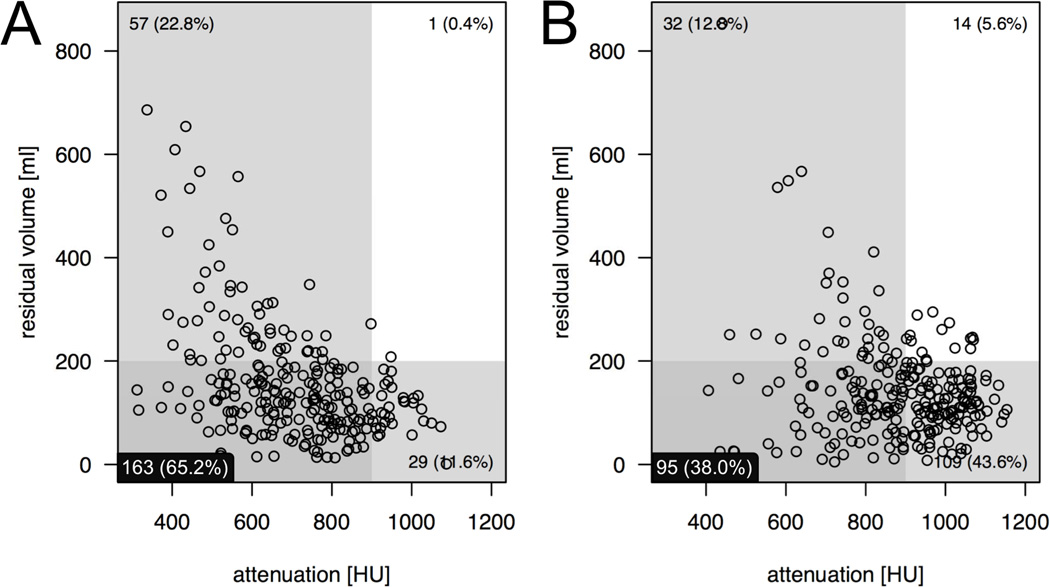
Figure 4.
Scatter plots illustrate the examinations that are optimal in terms of both volume (<200 ml, shaded horizontal box) and attenuation (300–900 HU, shaded vertical box) in the lower left quadrant. Simultaneously optimal fluid volume and attenuation was observed following (a) the MgC regimen in 163 examinations (65.2%) and following (b) the NaP regimen in 95 examinations (38%; p<0.001). There is an inverse correlation between volume and attenuation of residual colonic fluid for both regimens. This negative relationship is stronger for MgC (r=−0.444, p<0.001) than for NaP (r=−0.243, p<0.001).