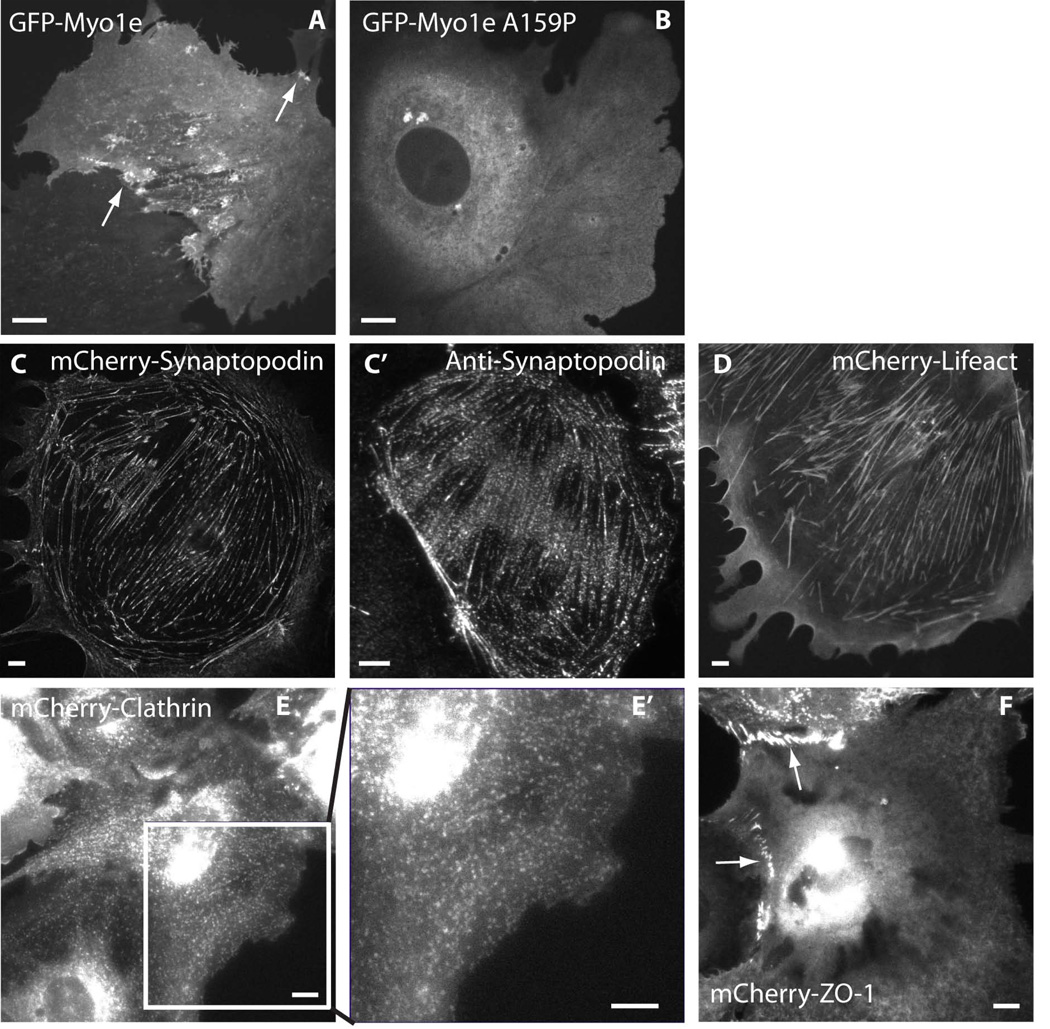
Figure 3. Localization of fluorescently labeled cytoskeletal markers in differentiated podocytes.
A, B, single confocal images showing localization of GFP-tagged wild type myo1e (A) and disease-associated myo1e mutant (B). A, arrows indicate myo1e localization to filopodia-like projections and vesicle-bound myo1e. B, myo1e mutant (A159P) does not localize to actin-containing projections or to vesicles. C–F, epifluorescence images showing localization of mCherry-tagged synaptopodin (C), Lifeact (D), Clathrin Light Chain (E), and ZO-1 (F) in differentiated podocytes. C’, immunostaining against endogenous synaptopodin in a differentiated podocyte. E’: enlarged image of the boxed region in E. Arrows in F point to cell-cell junctions, where ZO-1 is enriched. Viral concentrations used to infect podocytes were 105 PFU/ml for all constructs. Scale bars: 10 µm.