Figure 1. Schematic drawing of the inner ear and endolymphatic hydrops as a mechanism for Meniere's disease.
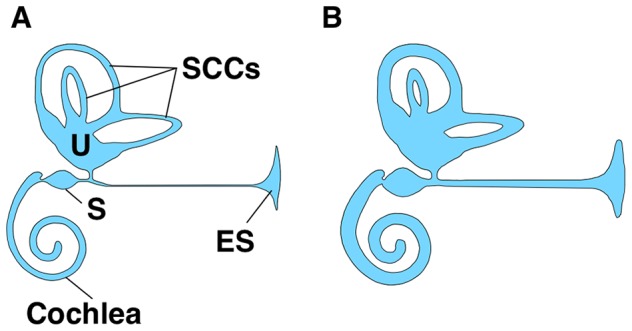
The inner ear consists of the cochlea, vestibule, and endolymphatic sac (ES). The utricle (U), saccule (S), and semicircular canals (SCCs) form the vestibule. A. Normal inner ear structure. B. Endolymphatic hydrops in patients with Meniere's disease.
