Figure 1.
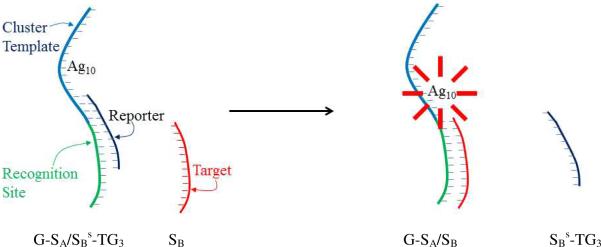
Representation of the strand exchange process using the bifunctional sensor strand with a template sequence for the silver cluster (blue) and a recognition site (green) for the target strand (red). The bridging quencher strand (black) statically quenches emission from a fraction of the clusters bound to the DNA host. After the quencher is displaced by the target, emission from the near-infrared emissive silver cluster is enhanced by a proportional increase in the number of emitting species. This population shift could be associated with a greater accessibility of the favored cluster binding site when the target binds.
