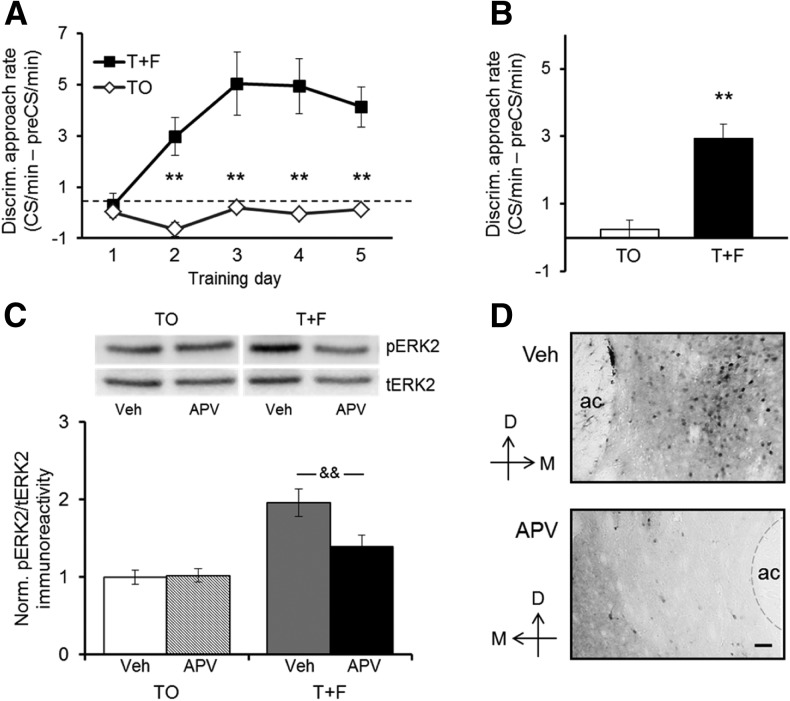
Figure 2.
NMDA receptor blockade in the NAc disrupts conditioned cue-evoked ERK activation. (A) Discriminative food cup approach during daily training sessions for rats in the Tone + Food group (T + F; n = 9) and the Tone-only control group (TO; n = 10). T + F rats preferentially approached the food cup during the tone (CS) compared with the preCS period, whereas TO controls did not exhibit discriminative approach behavior. Values show group means ± SEMs. (**) P < 0.01 for between-group comparisons. (B) Discriminative approach behavior during the CS-only test, immediately after infusion of APV (1 µg/0.5 µL) into one NAc and vehicle solution (150 mM NaCl, 0.5 µL) into the other NAc. Unilateral intra-NAc NMDA receptor blockade had no effect on discriminative approach behavior by the T + F group. Values show group means ± SEMs. (**) P < 0.01. (C) ERK2 activation (pERK2 immunoreactivity relative to tERK2 immunoreactivity in the same sample) in NAc samples harvested from rats of the T + F group and the TO control group shortly after the CS-only test. Ratios of pERK/tERK immunoreactivity are expressed relative to the same ratio observed in vehicle-infused NAc samples from TO control rats included on the same membrane. Values show group means ± SEMs. (&&) P < 0.01 for within-group comparisons. Representative Western blots of the vehicle- and the APV-infused sides of a rat of the T + F group and a rat of the TO group are shown above. (D) Representative immunohistochemical image of pERK-immunoreactive cells in the NAc of a rat from the T + F group. (Top panel) NAc side infused with vehicle solution; (bottom panel) NAc side infused with APV. Similar differences in staining between the vehicle- and APV-infused sides were observed in other T + F rats (n = 3). Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Dorsal, (M) medial, (ac) anterior commissure. To help discern the border of the ac, a thin gray dashed line was added in some of the images.