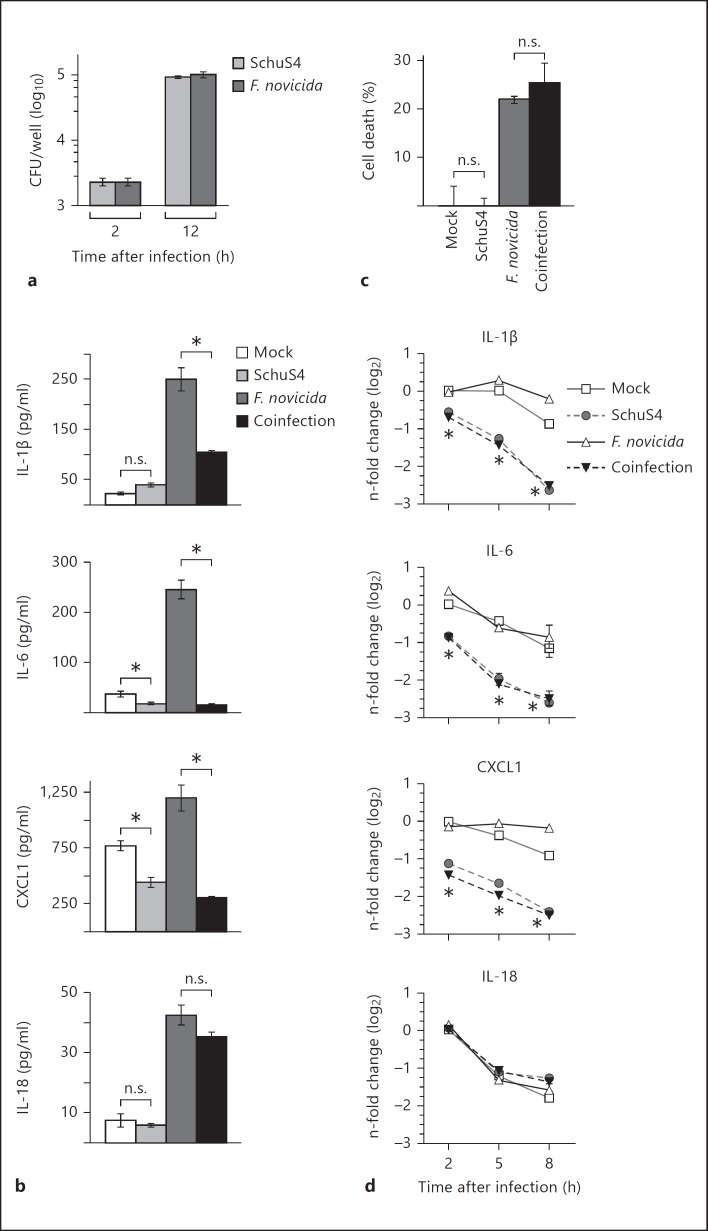
Fig. 1.
SchuS4 infection reduces IL-1β, IL-6 and CXCL1 RNA transcripts to inhibit cytokine/chemokine production in previously activated BMM. BMM were primed with P3C (500 ng/ml) and infected with SchuS4 MOI 50, F. novicida MOI 10 or coinfected with both SchuS4 MOI 50 and F. novicida MOI 10. Cells were infected with the indicated MOI to ensure equivalent uptake of F. novicida and SchuS4. Mock-infected cells served as negative controls. a Intracellular bacteria were enumerated at the indicated times after infection. b Supernatants were harvested 12 h after infection, and the quantity of IL-1β, IL-6, CXCL1 and IL-18 was measured by ELISA. * p < 0.05; n.s. = not significant when comparing the indicated groups. c Supernatants were harvested 12 h after infection, and lactate dehydrogenase levels were quantified to calculate the percentage of cell lysis. n.s. = Not significant compared to the indicated samples. d RNA was harvested at the indicated times after infection. qRT-PCR was performed to examine the quantity of the indicated transcripts, normalized to GAPDH. * p < 0.05, SchuS4 and F. novicida/SchuS4-coinfected cells compared to mock and F. novicida-infected cells. Each data point depicts the mean of triplicate samples. Error bars represent SEM. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.