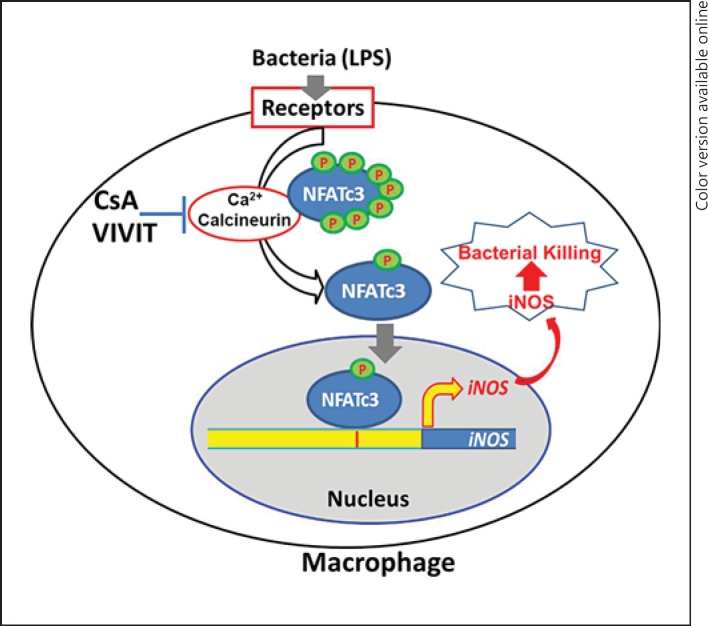
Fig. 6.
Transcription factor NFATc3 regulates macrophage bactericidal activity. During the onset of sepsis by bacterial infection, the transcription factor NFATc3 in macrophages is activated by the change in the calcium levels, which results in its translocation to the nucleus, resulting in the transcription of iNOS. This results in robust generation of NO and other reactive oxygen/nitrogen intermediates, resulting in efficient bactericidal activity and thus contributing to the resolution of harmful bacterial infection and inflammation.