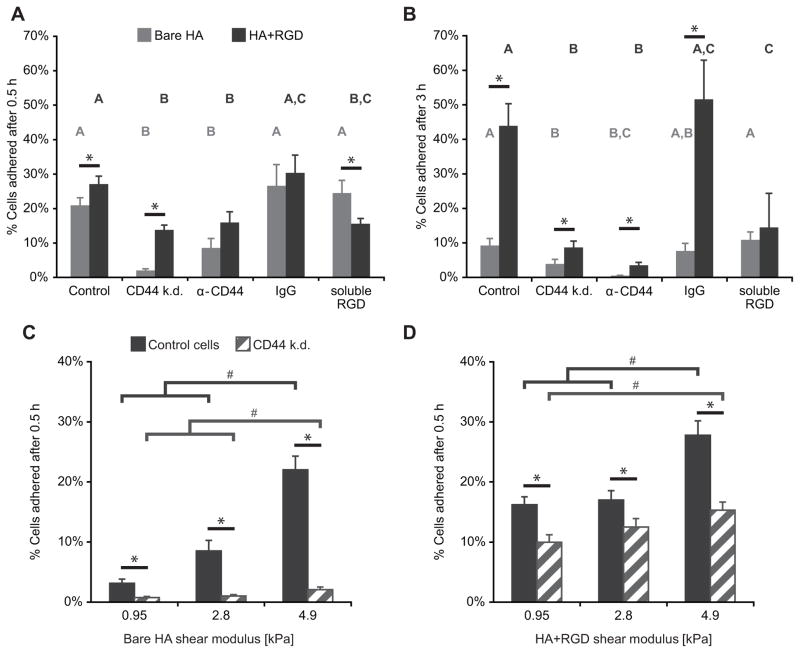
Figure 2. U373-MG cell adhesion to hyaluronic acid (HA) hydrogels is CD44- and stiffness-dependent.
(A) Adhesion of cells on 4.6 kPa hydrogels at short (0.5 h) time scales. Control cells or CD44 knockdown (k.d.) cells were allowed to attach to substrates in the absence or presence of adhesion blockers, including α-CD44 neutralizing antibody, IgG isotype control antibody, or soluble RGD peptide; then centrifuged to induce detachment of weakly adhered cells. (B) Adhesion of cells on 4.6 kPa hydrogels at longer (3 h) time scales. (C) Adhesion of cells on bare HA hydrogels as a function of stiffness after 0.5 h adhesion time. (D) Adhesion of cells on RGD-functionalized HA hydrogels as a function of stiffness after 0.5 h adhesion time. #p<0.05 differences between stiffnesses by Tukey-Kramer, *p<0.05 by Student’s t-test.