Figure 1.
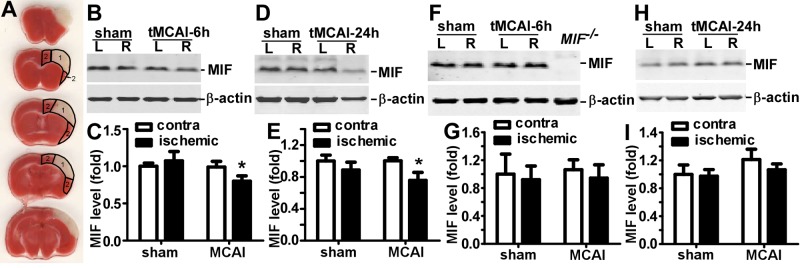
Reduced MIF expression in the infarct-targeted area after cerebral focal ischemia in mice. BALB/c mice were subjected to 2 h rMCAl, followed by 4 or 22 h of reperfusion or a sham procedure on the right hemisphere. The brain was freshly cut into 1 mm slices and subjected to TTC staining or protein expression analysis. A) At 22 h after reperfusion, infarcted tissue restricted to the MCA-supplied cerebral cortex was clearly distinguished by pale TTC staining and defined as the MCA territory (area 1) and the cortical peri-MCA area (area 2). B, D) At 6 h (B) or 24 h (D) after tMCAl, the MCA territory was lysed by RIPA-Doc buffer with 1% SDS. The lysate was resolved on a 12% Tris-tricine SDS-PAGE gel. MIF was detected by anti-MIF antibody, and β-actin was detected by β-actin antibody as control. C, E) Quantification of B and D, respectively. The ratio of MIF to β-actin was further normalized to unaffected hemisphere in sham-treated mice. Values are expressed as means ± sd, n = 6 for sham treatment and 7 for MCAl. *P < 0.05; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest. F, H) At 6 h (F) or 24 h (H) after tMCAl, the lysates of peri-MCA territory were subjected to 12% Tris-tricine SDS-PAGE. MIF and β-actin were detected by their respective antibodies. G, I) Quantification of F and H, respectively. The ratio of MIF to β-actin was normalized to unaffected hemisphere in sham-treated mice. Values are expressed as means ± sd, n = 6 for sham treatment and 7 for MCAl. P > 0.05; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni posttest.
