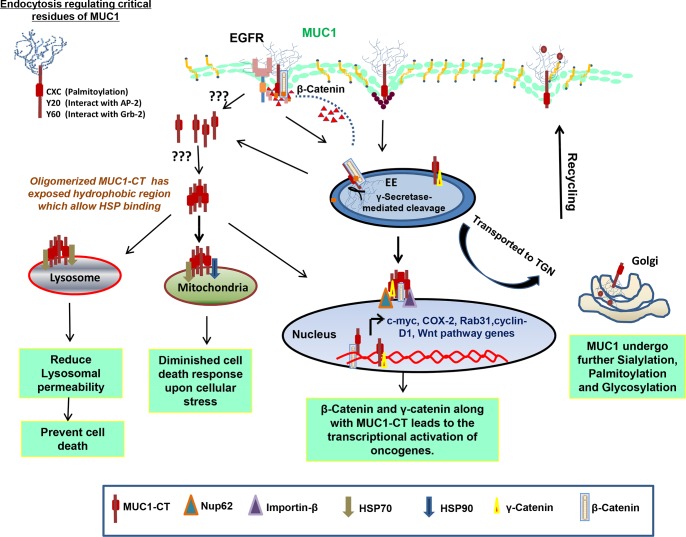
Figure 2. Mechanisms of intracellular transport and sorting of MUC1.
MUC1 has demonstrated to be internalization by using clathrin and caveolin-mediated pathway, which is dependent on Rab5a, an early endosome marker. MUC1 has many interacting partners including EGFR family proteins, AP-2, Grb2 and β-catenin. MUC1 possesses a γ-secretase cleavage site and get cleaved in early endosome: (A) Cleaved MUC1-C, which is still in contact with β-catenin, travels to nucleus to increase the transcription of various genes that are regulated by the TCF promoter; MUC1-C interacts with heat shock proteins for mitochondrial (B) and lysosomal (C) translocation resulting in reduced cell death response to DNA damage and cathepsin mediated apoptosis, respectively; (D) MUC1, like other glycoproteins, undergoes multiple rounds of sialylation and glycosylation while continuing on the itinerary to the Golgi. MUC1 also has a CQCRRK sequence motif, which undergoes palmitoylation. These post-translational modifications and interacting protein partners play important roles in deciding the fate of MUC1.