Figure 1. Subcellular localization of endogenous CIC isoforms in mammalian cells.
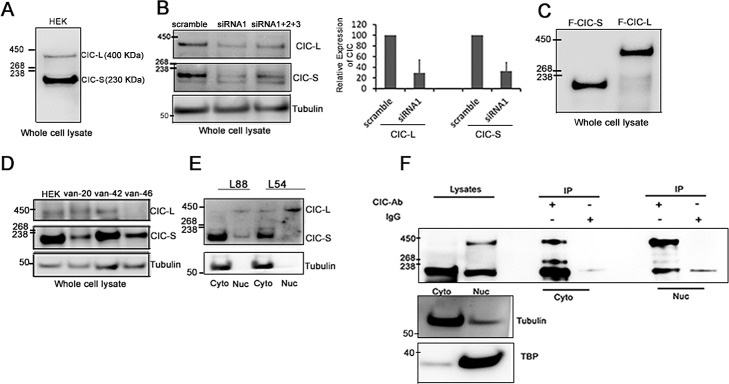
A. Western blots using an anti-CIC antibody detected CIC isoforms CIC-L (400 KDa) and CIC-S (250 KDa) in HEK cells. B. HEK cells were transfected with a single siRNA (siRNA1) or a three siRNAs in combination (siRNA1+2+3) against CIC. Reductions in CIC-S and CIC-L were detected after 72hrs using western blots. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Changes in band intensities for CIC-L and CIC-S after siRNA1 treatment relative to scramble siRNA were quantified using densitometry and averaged over three independent experiments to generate the bar graph. C. N-terminal FLAG fusions with CIC-S (F-CIC-S) and CIC-L (F-CIC-L) were ectopically expressed in HEK cells and detected using a FLAG antibody. D. Whole lysate preparations of gliomas (van-20: Glioblastoma, no IDH1 mutation, no 1p19q co-deletion; van-42 and van 46: oligodendroglioma, IDH1_R132H mutation, 1p19q loss) were probed for endogenous CIC expression using an anti-CIC antibody. E. Subcellular fractionations of ODG cell lines BT054 and BT088 were performed and cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions were isolated. Endogenous CIC isoforms were detected using western blots. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. CIC-S is enriched in cytoplasmic fractions and CIC-L is enriched in nuclear fractions. F. Cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions were isolated from HEK cells and endogenous CIC isoforms were isolated using immunoprecipitations (IPs) with an anti-CIC antibody. Subcellular localization of the isoforms was detected using a different anti-CIC antibody (by western blot analysis). Tubulin (Cyto) and TATA binding protein (TBP; Nuc) were detected as control proteins. Data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.
