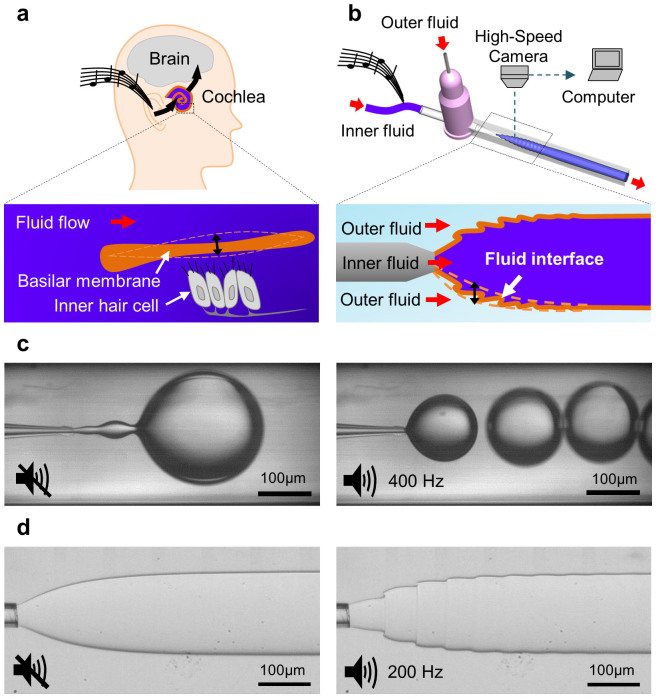
Figure 1. Schematics of hearing and the optical microscope images comparing jets with different interfacial tensions inside microcapillary devices.
(a) Schematic of hearing by human ear. (b) Schematic of hearing by the proposed “interfacial ear”. The inner and outer phases are driven by hydrostatic pressure. The tubing that directs the inner phase is attached on the membrane of a loudspeaker to introduce the vibration into the flow. (c) Optical microscope images of a co-flow of water-in-oil system in the jetting regime. Interfacial tension = 0.06 N/m. Left: No music is applied. Right: A musical note of 400 Hz is applied by a loudspeaker. (d) Visualization of the deformation of the passive interfaces in response to the applied vibration. Optical microscope images of a co-flowing jet with tripotassium phosphate and PEG constituting the inner and outer phase. Left: No external vibration is applied. Right: A musical note of 200 Hz is applied by a loudspeaker.