Fig. 1.
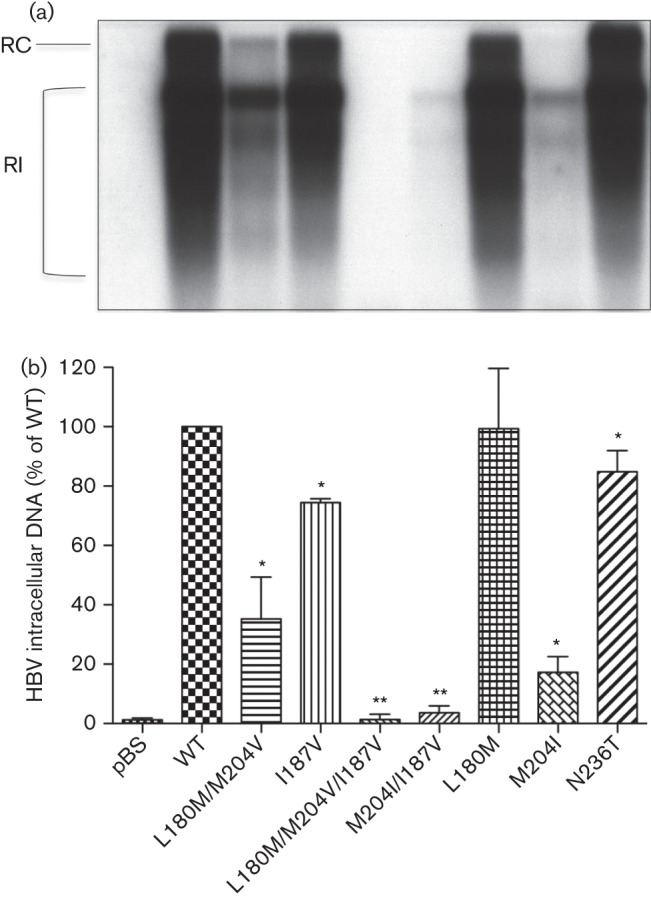
Intracellular replication capacity of HBV constructs. HepG2 cells were transiently transfected with replication-competent HBV constructs, and viral replication was assessed by HBV replicative intermediates after 4 days. Means and sd are given relative to WT. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (a) Intracellular replicative intermediates were analysed by Southern blot. (b) Quantification of HBV replicative intermediates. In comparison with WT, rtI187V and LAM-resistant mutations showed significantly impaired production of HBV replicative intermediates, while the reduction was even worse when rtI187V was introduced into HBV with LAM-resistant mutations. HBV replicative intermediates were quantified and normalized to the protein concentration of the cell lysates and β-Gal transfection efficiency. pBS, pBluescript vector; RC, relaxed circular; RI, replicative intermediates. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (compared with WT).
