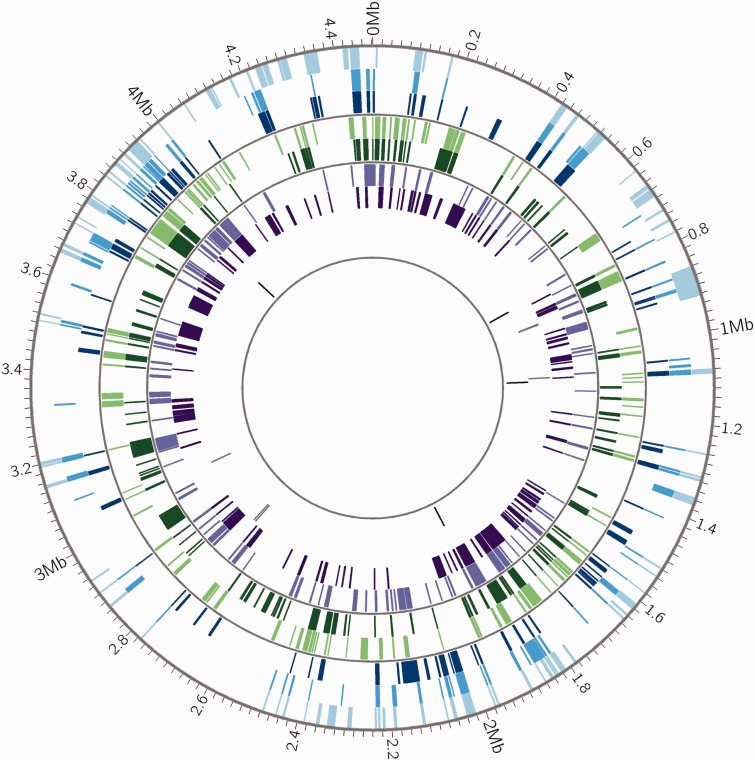
Fig. 3.—
Distribution of recombinant fragments across M. canettii chromosomes. Mycobacterium canettii recombinant fragments identified by BRATNextGen are shown as colored blocks. Genomic positions are in reference to M. canettii STB-A (CIPT 140010059). Mycobacterium canettii strain identifiers in order from outermost circle to innermost circle are STB-A (light blue), STB-D (medium blue), STB-E (dark blue), STB-L (light green), STB-G (dark green), STB-I (light purple), STB-H (dark purple), STB-K (gray), STB-J (black). Thin gray circles divide genomes into groups defined by phylogenetic analysis (supplementary fig. S5, Supplementary Material online). Prior to identification of recombinant fragments, regions prone to homoplasy such as PE/PPE genes and transposons were removed from the alignment. Plot made with Circos (Krzywinski et al. 2009). Recombinant DNA sequences are shared by closely related strains of M. canettii, which suggests that they are maintained in situ by clonal evolution following LGT events. This pattern is distinct from hot spots (see supplementary fig. S4, Supplementary Material online), which are shared across all strains. The frequency of recombination appears to vary among bacterial isolates, with two of the nine isolates (STB-K and STB-J) exhibiting little evidence of LGT.