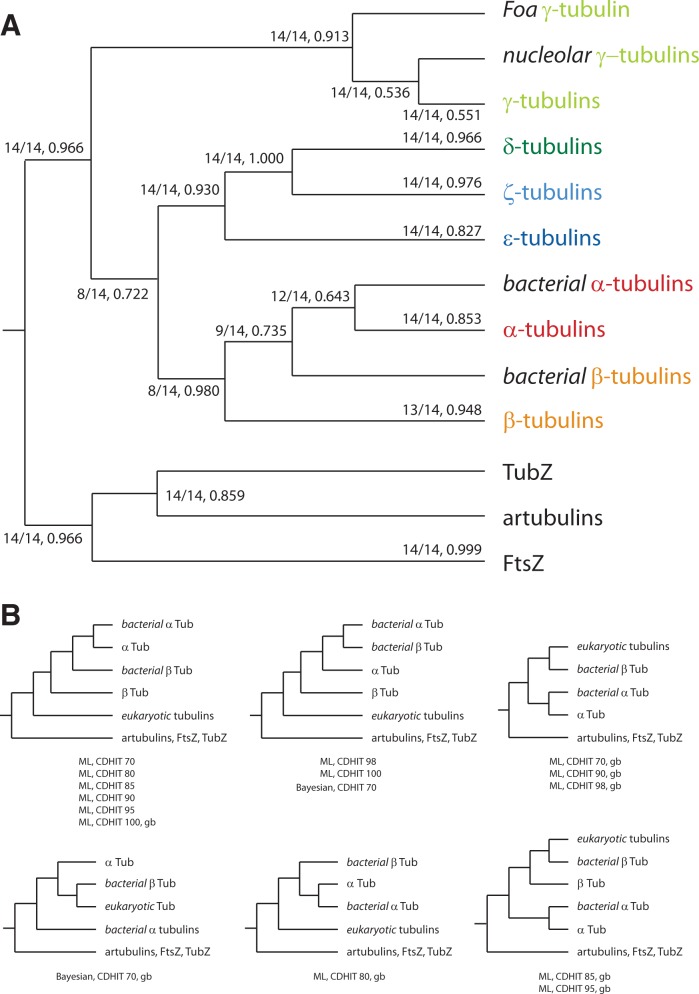
Fig. 2.—
Schematic tree of the tubulin subfamilies. (A) Schematic consensus tree from 14 trees reconstructed with the ML method and based on full and reduced data sets, in which redundant sequences, divergent regions, and unique positions were removed at various stringency levels. The first number at branches denotes the number of trees supporting the respective branch followed by the median of the support values (see supplementary table S2, Supplementary Material online, for more details). (B) The small trees show the alternative topologies for the branching of the bacterial tubulins. CDHIT, application of CD-Hit with the given similarity threshold; gb, use of gblocks.