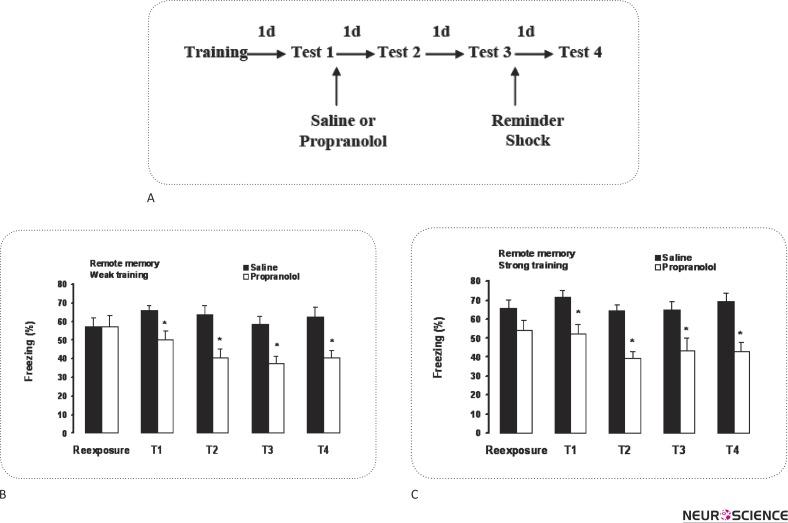
Figure 3.
Post-reactivation administration of propranolol impairs reconsolidation of remote contextual fear memories with either weak or strong strength. A: Schematic of the experimental design. Rats received either two or five footshocks. 36 days after training, the memory was reactivated with exposure of rats into the same conditioning box for 90s and immediately followed by saline or propranolol injections. Long-term memory was tested one (Test1), two (Test2), and three (Test3) days after memory reactivation. Propranolol impaired long-term memory with either weak (B) or strong (C) strength. Application of a weak reminder shock did not recover the original memory.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 as compared with saline-treated animals at the same test.