Abstract
Background
The main objectives of this study were to assess the current research and development of traditional Uighur medicine in Xinjiang (China), and to evaluate the promising pharmacological products of traditional Uighur medicine for further studies.
Materials and Methods
Traditional Uighur medicine data of medicine registry, patent, and academic publications was collected and analyzed.
Results
Data showed that, among the registered and studied traditional Uighur medicine, the main therapeutic areas of traditional Uighur medicine focused on skin disease, urogenital disease, rheumatism and digestive system disease. The representative traditional Uighur patent medicine included the following: BaixuanXiatare Tablets, Kaliziran Tincture and Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection (Psoriasis and vitiligo); Xi-payimazibiziLiquid (prostatitis); KursiKaknaq (urinary tract infection); Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules (anti-rheumatism medicine); HuganBuzure Granules (digestive system disease). Moreover, ten Uighur herbs were widely used, including: ResinaScammoniae, Folium FumicisDentati, HerbaDracocephali, Semen AmygdaliDulcis, HerbaChamomillae, FructusPimpinellaeanisi, Cortex Foeniculi, FructusVernoniae, FructusApii, and Radix AnacycliPyrethri.
Conclusion
This study concluded by indicating that traditional Uighur medicine with excellent curative effect should be screened in details for their phytochemical properties and pharmacological activity to discover new bioactive constituents.
Keywords: Traditional Uighur medicine, Traditional Uighur patent medicine, Uighur herb
Introduction
Traditional Uighur medicine (TUM) is one of the most important traditional medicines in Central Asia, which is rooted in the ancient Uighur medicine theory and has a history of more than 2,500 years. Currently, TUM is mainly applied over Central Asia, North Africa and South Europe (Wang et al., 2005). The traditional theory of Uighur medicine regards that the nature is constituted by four substances: fire, air, water, and earth (Amat et al., 2009; Geng, 2006). Built upon this theory, TUM in Xinjiang Province (China) has also combined the essence of other medical theories, such as traditional Chinese medicine, ancient Greece medicine, Egyptian medicine, Arabian medicine, and Indian medicine. It has formulated a profound theoretical system, which is composed of the four temperaments (hot, cold, moist, and dry) and the four body fluids (Kan (blood), Belghem (phlegm), Sapra (yellow bile), and Savda (black bile) (Upur et al., 2011). The theory of body fluids came from the ancient Unani medicine theory, the humorism. Based on the Humorae theory, TUM has emphasized the balance status of four temperaments and that conditioning of the body fluids has become the main therapeutic principles (Upur et al., 2011).
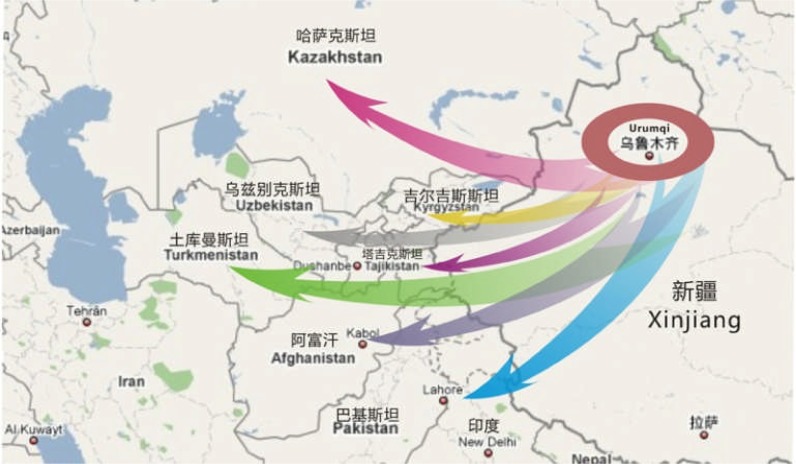
Based on its complete medical theory system, TUM in Xinjiang has accumulated rich clinical experiences in the past. In treating intractable diseases, TUM has shown distinguished medical methods and unique therapeutic effect. As a traditional ethnic medicine, TUM has made great contribution to not only the health care in Xinjiang but also the medical treatment around China. Moreover, it has benefited the people in the other countries of Central Asia, with their intimate collections of religious beliefs and language (see Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Location of Xinjiang in Central Asian
Despite its special medical contribution to patients, TUM in Xinjiang has not received the attention it deserves in modern research and development. Thus, this study aims at assessing the current research and development of Uighur medicine in Xinjiang thorough studying its registry, patent, and publications, hoping to provide inspiring knowledge about new pharmacological products of Uighur medicine.
Materials and Methods
Data source and collection
To provide comprehensive analysis of TUM in Xinjiang, this study targeted not only traditional Uighur patent medicine (TUPM) but also Uighur herbs. TUPM are prescription preparations that follow the traditional Uighur medicine theory, which have been applied in medical treatment historically. Data of registry, patent and academic publication of TUM in Xinjiang was identified as main data types. All the data was searched and obtained from specific databases. Because the research of TUM is still at a primary stage and most of researches are from China, this study mainly focused on databases in China.
Firstly, the registry database of CFDA (China Food and Drug Administration) was used to search and screen the registered TUPM. The standard names of these TUPM were adopted from the Drug Standard of Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China (Uighur Medicine Part), which was edited by The Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China as a legal basis for TUM's manufacturing, sales, usage, and administration.
Secondly, the China Medicine Patent Database in China Intellectual Property Right Net (CNIPR) was used to search patents of TUPM and Uighur herbs. TUPM's name and formulation were searched by “ABSTRACT” in the database to identify target patents. For Uighur herbs, only herb name was used.
Thirdly, the academic publication data of TUPM and Uighur herbs were retrieved in the China National Knowledge Internet (CNKI). Both TUPM and Uighur herb were searched by name, with retrieval strategy as “SU= a medicine's name”.
Data analysis
Data analysis was conducted in sequence. Firstly, we analyzed the information of registered TUPM, mainly focusing on therapeutic area, dosage and formulation. Secondly, patents and academic
ublications of TUPM were analyzed. For patents, analysis focused on patent's name, type and therapeutic area; for academic publications, analysis concentrated on paper quantity and research content. Thirdly, the ten Uighur herbs mostly used in TUPM were analyzed by similar analysis strategy of TUPM.
Results
Registry of TUPM
Data showed that 43 TUPMs listed in the Drug Standard of Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China (Uighur Medicine Part, 2000 edition) had got official approval (see Table 1). For therapeutic areas, these TUPMs were mainly used for treating skin, urogenital system and digestive system diseases. Among these registered TUPMs, there are11 TUPMs treating skin disease, including Compound Siyadan Tincture, Qubaimaribairesi Pills, BaixuanXiatare Tablets, Compound Muni Ziqi Granules, QubaiBabuqi Tablets, Compound Vernoniaanthelmintica Pills, Kaliziran Tincture, Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection, Suziafu Tablets, and Yangxindawayimixikemi Unguent. And 10 TUPMs are related to treat genitourinary system diseases, including Qiangshenluobofusaiheli Unguent, Wenshensulafu Tablets, Gujingmaisiha Tablets, Xi-payimazibizi Liquid, KursiKaknaq, Yanxiaodinaer Syrup, QingreKasen Granules, Luobufukebiri Tablets, Yimusake Tablets, and Jinsuokunduer Tablets. Additionally, 7 TUPMs are about treatment of digestive system diseases, including Mamuran antidiarrheal l Capsules, QizilGulqent, Xipayi mouth rinse, Rose Oral Liquid, Tongzhiaitilefeilisana Tablets, HuganBuzure Granules, Sanhanyao Tea, and Compound Gaoziban Tablets.
Table 1.
TUPM approved by CFDA (By therapy through ranking)
| Therapeutic area |
Local Uighur name |
Dosage form |
Prescription | Bases | Taxonomical details | Plant parts used | |
| 1 | Skin disease | Compound Vernoniaanthel mintica Pills |
Pill | Y |
FructusVernoniae Radix Anacycli Pyrethri Rhizoma Zingiberis, |
Asteraceae, Vernonieae Asteraceae, Anthemideae Amomum zingiber |
Mature fruit Root Dried rhizome |
| Radix | Convolvulaceae, | Root | |||||
| OperculinaeTurpethi | Operculina | ||||||
| 2 | Skin disease | Qubaimaribaire si Pills |
Pill | N |
BungarusParvus ResinaScammoniae |
Elapidae, Bungarus Convovulus scammonia |
Dried body Emulsion exudates of the roots |
| Stigma Croci | Crocus sativus | Stigma | |||||
| Stigma Croci | Crocus sativus | Stigma | |||||
| Semen | Loganiaceae, Strychnos | Dry ripe seed | |||||
| StrychiNux-vomicae | |||||||
| Scorpio | Arachnida, Scorpiones | Dried body | |||||
| Aloe Varae | Xanthorrhoeaceae, | Herb | |||||
| Asphodeloideae | |||||||
| Rana Ridibunda | Rana, Ranidae | Dried body | |||||
| Gekko | Gekkonidae, Gekko | Dried body | |||||
| Boswellia carterii | Burseraceae, Boswellia | Resin | |||||
| Rhizoma Aeori Calami | Acorus calamus | Rhizoma | |||||
| 3 | Skin disease | BaixuanXiatare Tablets |
Tablet | N |
Herba Euphorbiae Humifusae, |
Euphorbia, humifusa | Herb |
| Fructus Chebulae, | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Mature fruit | |||||
| Resina Scammoniae | Convovulus scammonia |
Emulsion exudates of the roots |
|||||
| Aloe Varae |
Xanthorrhoeaceae, Asphodeloideae |
Herb | |||||
| 4 | Skin disease | QubaiBabuqi Tablets |
Tablet | Y |
Fructus Psoraleae Fructus Vernoniae |
Fabaceae, Psoralea Asteraceae, Vernonieae |
Mature fruit Mature fruit |
|
Rhizoma Alpiniae Officinarum |
Zingiberaceae, Alpinia | Rhizoma | |||||
|
Herba Operculinae Turpethi |
Convolvulaceae, Operulina |
Herb | |||||
|
Radix et Herba Plumbaginis Zeylani-cae |
Plumbaginaceae, Plumbago |
Root | |||||
| 5 | Skin disease | Vernoniaanthel mintica |
Injection | Y | Fructus Vernoniae | Asteraceae, Vernonieae | Mature fruit |
| Injection | |||||||
| 6 | Skin disease | Compound | Tincture | N | SemenNigellae | Ranunculaceae | Dry ripe seed |
| Siyadan | Ganduliferae | ||||||
| Tincture | Semen Persicae, | Rosaceae, Prunus | Dry ripe seed | ||||
| Fructus Granati | Pomegranate, Granatum | Mature fruit | |||||
| 7 | Skin disease | Kaliziran | Tincture | Y | Fructus Vernoniae | Asteraceae, Vernonieae | Mature fruit |
| Tincture | Fructus Psoraleae | Fabaceae, Psoralea | Mature fruit | ||||
| Radix Polygni Multiflori | Knotweed, Fallopia | Root tuber | |||||
| Radix Angelicae Sinensis | Apiaceae, angelica | Root | |||||
| Radix Sapshnikoviae, |
Umbelliferae, Saposhnikovia |
Root | |||||
| Fructus Cnidii | Umbelliferae, Cnidium | Mature fruit | |||||
| Cortex Dictamni | Rutaceae | Peel | |||||
| Fructus Mume | Rosaceae, Prunus |
Near mature fruits |
|||||
| Semen sinapis | Cruciferae, Sinapis | Dry ripe seed | |||||
| Flos Caryophylli | Myrtaceae, caryophyllata | Flower bud | |||||
| 8 | Skin disease | Compound Siyadan Tonic |
Liniment | N |
Semen Nigellae Ganduliferae |
Ranunculaceae | Dry ripe seed |
| Semen Persicae | Rosaceae, Prunus | Dry ripe seed | |||||
| FructusGranati | Pomegranate, Granatum | Mature fruit | |||||
| 9 | Skin disease | CompoundMun | Granule | Y | Herba cichorii | Asteraceae, Cichorieae | Herb |
| i Ziqi Granules | Cortex Foeniculi | Umbelliferae, Foeniculum | Peel | ||||
| Cichorium intybus L. | Asteraceae, Cichorium | Herb | |||||
| Fructus Apii | Umbelliferae, Apium | Mature fruit | |||||
| Herba Dracocephali | Labiatae, Dracocephalum | Herb | |||||
| Semen Nigellae | Ranunculaceae | Dry ripe seed | |||||
|
Ganduliferae, Radix Glycyrrhizae |
Leguminosae, Glycyrrhiza | Root and rhizome | |||||
| Herba Chomomollae | Malavaceae, Althaea | Herb | |||||
|
Herba Cymbopogonis Citrari |
Poaceae, Cymbopogon | Herb | |||||
| Fructus Ocimi Basilici | Ocimum, basilicum | Mature fruit | |||||
| Fructus Pimpinellae Anisi | Umbelliferae, Pimpinella | Mature fruit | |||||
| 10 | Skin disease,Cardiovascular Disease |
Suziafu Tablets | Tablet | N |
Herba Cymbopogonis Distantis Radix Arnebiae Euchroma Herba Absinthii |
Poaceae, Cymbopogon Boraginaceae, Arnebia Asteraceae, Artemisia |
Herb Root Hherb |
| 11 | Skin disease,Cardiovascular Disease |
Yangxindawayi mixikemi Unguent |
Soft Extract |
Y |
Lignum Santali Albi Moschus |
Santalaceae, Santalum Cervidae, Cervus |
Lignum Dry secretion in sachet of mature male Moschus |
| StigmaCroci. | Iridaceae, Crocus | Heartwood | |||||
| ConcretioSiliceaBambusae | Gramineae, Bambusa |
Cube after the liquid secretion inside of haulm dried of plant |
|||||
| Flos Anchusae | Verbenaceae, Callicarpa | Flower | |||||
|
Margarita Succinum |
Pteriidae |
The resin of Pinus plants, buried under the earth for long years and concreted and transformed to sulfhydryl compound |
|||||
|
Aurum Foil, Argentum Foil Incuabulum Bombycis |
Bombycidae |
Native gold Native silver Cocoon shell of silk cocoon |
|||||
| Mastiche | Burseraceae, Boswellia |
Aromatic resin of the mastic tree |
|||||
|
Lignum Aquilariae Resinatum |
Thymelaeaceae, Aquilaria | Resinous wood | |||||
| 12 | Genitourinary System Disease |
Luobufukebiri Tables |
Tablet | Y |
Pinus bungeana, Fructus Dauci Sativae Penis Bovis |
Pinaceae, Pinus Apiaceae, Daucus Bovidae |
Not known Mature fruit Dry penis and testicles of Bostaurus domesticus |
|
Semen Amygdali Dulcis Semen Brassicae Rapae Semen Cocois Stigma Croci. Arillus Myristicae Mesua ferrea L. Semen Medicaginis Limoniumgmelinii (Wildl.) Kuntze, etc. |
Rosaceae, Amygdalus Cruciferae, Brassica Alliaceae, Allicea Crocus sativus Myristicaceae, Myristica Guttiferae, Mesua Fabaceae, Medicago Chenopodiaceae, lljinia |
Dry ripe seed Dry ripe seed Dry ripe seed Stigma Dry aril Not known Dry ripe seed Not known |
|||||
| 13 | Genitourinary System Disease |
Wenshensulafu Tablets |
Tablets | N |
Tuber Salep, Semen Myristicae, Rhizoma Alpiniae Officinarum Radix Aconiti Lateralis Preparata Arillus Myristicae Cortex Cinnamomi Papaversom niferum L. Stigma Croci. |
Orchidaceae, Bletilla Myristicaceae, Myristica Zingiberaceae, Alpinia |
Tuber Dry ripe seed Rhizome Secondary root Dry aril Bark Pericarpium stigma |
| 14 | Genitourinar y System Disease |
Gujingmasiha Tablets |
Tablet | N |
Radix Anacycli Pyrethri Mastich |
Asteraceae, Pyrethrum Burseraceae, Boswellia |
Root Aromatic resin of the mastic tree |
|
Fructus Cardamomi Rhizoma Cyperi Stigma Croci., Semen Myristicae Radix Curcumae Wenyujin Flos Caryophylli Radix et Rhizoma Nardostachycis Fructus Tsaoko Flos Rosae Rugosae |
Zingiberaceae, Amomum Cyperaceae, Cyperus Crocus sativus Myristicaceae, Myristica Zingiberaceae, Curcuma Myrtaceae, Eugenia Valerianaceae, Nardostachys Zingiberaceae, Amomum Rosaceae, rosa |
Mature fruit Rhizome Stigma Dry ripe seed Root tuber Flower bud Root and rhizome Mature fruit Flower bud |
|||||
| 15 | Genitourinar y System Disease |
KursiKaknaqyi | Tablet | Y |
Herba Physalis Alkekengi Semen Cucumeris Resina Draconis |
Spamaceae, Physalis Cucurbitaceae, Cucumis Palmae, Daemonorops |
Herb Dry ripe seed Processed resin effused by the fruit |
|
Gum tragacanth Ummi Rabicum Semen Amygdali Dulcis Radix Glycyrrhizae Boswellia carterii Frcutus Apii Opium |
Leguminosae, Astragalus Mimosaceae, Acacia Rosaceae, Amygdalus Leguminosae, Glycyrrhiza Burseraceae, Boswellia Umbelliferae, Apium Papaveraceae, papaver |
Processed gum Processed gum Dry ripe seed Root and rhizome Resin Mature fruit Extract of fruit Roots |
|||||
| 16 | Genitourinary System |
Yimusake Tablets |
Tablet | Y |
Tuber Salep Moschu |
Orchidaceae, Bletilla Secretions |
Extract of fruit Roots Animal glands |
| Disease | AmberaGrisea | Iridaceae, Crocus |
Digestive Secretions |
||||
| Stigma Croci. | Loganiaceae, Strychnos | Pistil | |||||
| Semen | Seeds | ||||||
| StrychiNux-vomicae | |||||||
| Boswelliacarterii | Resin | ||||||
| Penis Bovis | Bullwhip | ||||||
| Semen Myristicae | Myristicaceae, Myristica | Fruit | |||||
| FlosCaryophylli, | Myrtaceae, Syzygium | Buds | |||||
| RhizomaAlpiniaeOfficinarum | Papaveraceae, Papaver | poppy capsule | |||||
| Papaversomniferum L. | Zingiberaceae, Alpinia | Rhizome | |||||
| 17 | Genitourinar y System Disease |
Xi-payimazibizi Liquid |
Mixture | Y | Fructus Mori | Moraceae, Moraceae | Fruit |
| Semen Euryales | Nymphaeaceae, Euryale | Seeds | |||||
|
RhizomaDioscoreaeSepte mloba e |
Dioscoreaceae | Tuber | |||||
| FructusRosaeLaevigatae | Rosaceae, Rosa | Fruit & seeds | |||||
| FructusGardeniae | Rubiaceae, Gardenia | Fruit | |||||
| 18 | Genitourinary | Qiangshenluob | Soft | Y | Pinusbungeana | Pinaceae, Pinaceae | pine cone |
| System | ofusaiheli | Extract | Pistaciavera L. | ||||
| Disease | Unguent | ||||||
|
Semen Coryli, Semen AmygdaliDulcis, Papaversomniferum L., Herbalamiibarbati, Semen Melo, Semen Fraxini, Cortex Cinnamomi, |
Anacardiaceae, Pistacia Betulac, Corylus Rosaceae, Prunus Papaveraceae, Papaver Labiatae, Lamium |
Fruit Fruit Fruit Seeds Herb |
|||||
| Limoniumgmelinii (Wildl.) |
Cucurbitaceae, Cucumis Oleaceae, Ligustrum Lauraceae, Cinnamomum |
Seeds Fruit limb |
|||||
| Kuntze | Plumbaginaceae, Limonium | Herb | |||||
| Semen Cucumeris, Radix | Cucurbitaceae | Seeds | |||||
| CentaureaRuthenica, etc. | Asteraceae, Centaurea | Root | |||||
| 19 | Genitourinar y System |
Yanxiaodinaer Syrup |
Syrup | Y | FlosNymphaeae |
Nymphaeaceae, Nymphaea |
Flower |
| Disease |
Radix cichorii Fructus cichorii FlosRosaeRugosae Rhizoma et Radix RheiPalmat Folium FumicisDentati, Semen CuscutaeChinensis |
Asteracea, Cichorium Asteracea, Cichorium Rosaceae, Rosaceae Apiaceae, Ligusticum Polygonacea, Rheum Boraginaceae, Anchusa Convolvulaceae, Cuscuta |
Roots Fruit flower Herb Root Herb Herb |
||||
| 20 | Genitourinar y System Disease |
QingreKasen Granules |
Granule | Y | Herbacichorii | Asteraceae, Cichorium L. | Herb |
| 21 | Genitourinary | Jinsuokunduer | Tablet | N | Boswelliacarterii | Burseraceae, Boswellia | resin |
| System | Tablets | Rhizoma Cyperi | Cyperaceae, Cyperus | Stem | |||
| Disease | Radix Aucklandiae | Rosaceae | Stem | ||||
| Digestive System Disease |
FructusQuerciAcutissimae RhizomaZingiberis Piper nigrum L. |
Fagaceae, Quercus Zingiberaceae, Zingiber Piperaceae, Piper |
Seeds Roots Seeds |
||||
| 22 | Digestive | Tongzhiaitilefei | Tablet | N | Folium Sennae | Leguminosae, senna | foliage |
| System | lisana Tablets | PhyllanthiFructus | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||
| Disease | FructusChebulaeImmaturus | Phyllanthace, Phyllanthus | Fruit | ||||
| FructusChebulae | Combretacea, myrobalan | Fruit | |||||
| FructusTerminaliaeChebulae | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||||
| 23 | Digestive System |
Tongzhiaitilefei lisana Tablets |
Tablet | N | GallaTurcica | / | Larva |
| Digestive | |||||||
| 24 | Digestive System Disease |
Rose Oral Liquid |
Mixture | N | FlosRosaeRugosae | Rosaceae, Rosaceae | Flower |
| 25 | Digestive System Disease |
Mamuranantidi arrheal Capsules |
Capsule | Y |
RhizomaCoptidis ResinaDraconis, Boswelliacarterii |
Ranunculacea, Coptideae palmae Burseraceae, Boswellia |
Rootstock Resin Resin |
|
GallaTurcica FlosGranati |
/ Lythraceae, Punica |
Larva Pericarp |
|||||
|
ConcretioSiliceaBambusae Semen PlantaginisPsyllii |
Hypocreaceae, tabaxir | Fungus | |||||
| Semen PlantagtinisPsyllii |
Plantaginaceae, Plantago L |
Herb | |||||
|
FructusChebulaeImmaturus FructusCoriandri |
Phyllanthaceae, Phyllanthus Apiaceae, corainder Combretacea, Quisqualis Berberidaceae, Berbens Rosaceae, Rosaceae |
Fruit Herb Fruit Rootstock Flower |
|||||
| 26 | Digestive System Disease |
Qizil Guliqent | Soft Extract |
N | FlosRosaeRugosae | Rosaceae, Rosaceae | Flower |
| 27 | Digestive System Disease |
HuganBuzure Granules |
Granule | Y |
FructusApii, Herbacichorii Semen Cuscutae Chinensis. |
Umbelliferae, celery Asteraceae, Cichorium L. Convolvulaceae, Cuscuta europaea |
Seeds Herb Herb |
| Radix Api | umbelliferae, celery | Roots | |||||
| Cortex Foeniculi |
Umbelliferae, Foeniculum Mill. |
Roots | |||||
| Cichoriumintybus L. | / | / | |||||
| 28 | Digestive System Disease,mus culoskeletal system (rheumatism) |
Sanhanyao Tea | Liniment | N | FructusFoeniculi | Asteraceae, Cichorium L. | Roots |
| Fructus Cardamomi |
Zingiberaceae, Elettaria Maton |
Seeds | |||||
| Valerianaofficinalis Linn. | Valerianaceae,Valeriana | Herb | |||||
| FructusPimpinellaeAnisi | Apiaceae, Pimpinella | Seeds | |||||
| Cortex Cinnamomi | Lauraceae, Cinnamomum | Rind | |||||
| FructusTsaoko |
Zingiberaceae, Amomum L. |
Fruit | |||||
| FructusCinnamomi | Lauraceae, Cinnamomum | Fruit | |||||
| RhizomaAlpiniaeOfficinarum | Zingiberaceae, Alpinia | Roots | |||||
| FructusPiperisLongi | Piperaceae, Piperaceae | Cluster | |||||
| FlosCaryophylli | Oleaceae, Oleaceae | Flower | |||||
| FructusFoeniculi |
umbelliferae, Foeniculum Mill |
Seeds | |||||
| FructusApii | umbelliferae, celery | Seeds | |||||
| FructusGardeniae | Rubiaceae, Gardenia | Fruit | |||||
| 29 | Respiratory System Disease |
ResaiBisitan Granules |
Granule | Y | FructusCordiaeDichotomae, | Boraginaceae, Cordia | Fruit |
| FructusJujubae | Rhamnaceae, Ziziphus | Fruit | |||||
| Papaversomniferum L. | Papaveraceae, Papaver |
Pericarpium papaveris |
|||||
| Radix Glycyrrhizae | Fabaceae, Glycyrrhiza | Root | |||||
| FructusAlthaeaeRoseae | Malvaceae, Alcea | Seeds | |||||
| Semen Cucumeris |
Cucurbitaceae, Cucumis Linn |
Seeds | |||||
| Semen Cydoniae | Rosaceae, Cydonia | Seeds | |||||
| Semen AmygdaliDulcis | Rosaceae, Prunus | Seeds | |||||
| Papaversomniferum L. | Papaveraceae, Papaver | Seeds | |||||
| Radix Glycyrrhizae | Fabaceae, Glycyrrhiza | Roots | |||||
| UmmiRabicum | Leguminosae, Acacia | Gum | |||||
| 30 | Respiratory System Disease |
Zukamu Granules |
Granule | Y | RhizomaKaempferiae |
Zingiberaceae, Kaempferia |
Stem |
| FlosNymphaeae |
Nymphaeaceae, Nymphaea |
Flower | |||||
| FructusCordiaeDichotomae | Boraginaceae, Cordia | Fruit | |||||
| HerbaMenthae | Lamiaceae, Mentha L. | Lea | |||||
| FructusJujubae | Rhamnaceae, Ziziphus | Fruit | |||||
| HerbaChomomollae | Compositae, Anthemis | Flower | |||||
| Radix Glycyrrhizae | Fabaceae, Glycyrrhiza | Roots | |||||
| Semen AlthaeaeRoseae | Malvaceae, Alcea | Seeds | |||||
|
Rhizoma et Radix RheiPalmat |
Polygonaceae, Rheum | Roots | |||||
| Papaversomniferum L. | Papaveraceae, Papaver |
Pericarpium papaveris |
|||||
| 31 | Respiratory System Disease |
Hanchuanzupa Granules |
Granule | Y | HerbaHyssopi | Labiatae, Hyssopus | Lea |
| Herbaadianticaudati | Adiantaceae, Adiantum | Hibiscus trionum | |||||
| Radix Glycyrrhizae | Fabaceae, Glycyrrhiza | Root | |||||
| FructusFoeniculi | Apiaceae, Foeniculum | Fruit | |||||
| FructusApii | Apiaceae, Apium | Fruit | |||||
| Semen Trigone | Fabaceae, Trigonella | Seeds | |||||
| HerbaCymbopogonisDistantis | Rutaceae, Ruta | Lea | |||||
| FlosRosaeRugosae | Rosaceae, Rosa | Flower | |||||
| Semen Urticae | Urticaceae, Urtica L | Seeds | |||||
| 32 | Blood System |
Kebireti Tablets | Tablet | Y | Sulfur | Sulphur | Crystal |
| UmmiRabicum, | Leguminosae, Acacia | Gum | |||||
| Sal-Ammoniac | Sal-Ammoniac | Crystal | |||||
| Radix AnacycliPyrethri |
Asteraceae, Chrysanthemum |
Roots | |||||
| Poria | Fomitopsidaceae,Wolfiporia | Sclerotium | |||||
| 33 | Blood System |
GangkangMukuli Tablets |
Tablet | N | Com-miphoramukul | Burseraceae | Resin |
| Succinum | Ambrum | Resin | |||||
| OsCorallii | Agariciidae |
Calcareous skeleton |
|||||
|
Concha MargaritiferaUsta |
Nacre | Powder | |||||
| FructusChebulae | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||||
| FructusTerminaliaeChebulae, | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||||
| PhyllanthiFructus | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||||
| FructusChebulaeImmaturus |
Phyllanthaceae, Phyllanthus |
Fruit | |||||
| 34 | Blood System |
Xueninganjipaer Syrup |
Mixture | Y | RhizomaPolygoniBistortae | Polygonaceae, Polygonum | Stem |
| 35 | Cardiovascular System |
Aiweixin Liquid |
Mixture | N | IncuabulumBombycis | Silkworm cocoon | Silkworm cocoon |
| HerbaAnchusae, |
Boraginaceae, Lycopsis, Echium |
Lea | |||||
|
Radix et RhizomaNardostachycis |
Caprifoliaceae, Nardostachys |
Roots and rhizomes |
|||||
| Flos Salix Caprea | Salicaceae, Salix | Flower | |||||
| Moschus | Moschus | Sachet | |||||
| Stigma Croci. | Iridaceae, Crocus | Stigma | |||||
| HerbaDracocephaliMoldavicae | Labiatae, Dracocephalum | Hibiscus trionum | |||||
| HerbaLavandulae | Lamiaceae, Perilla L. | Seeds | |||||
| FlosAnchusae |
Boraginaceae, Lycopsis, Echium |
Flower | |||||
| FructusCardamomi |
Zingiberaceae, Elettaria Maton |
Seeds | |||||
| Usnea | Usneaceae, Usnea | Thallus | |||||
| 36 | Cardiovascular System |
YixinBadiranjibuya Granules |
Granule | N | FlosRosaeRugosae, etc. | Rosaceae, Rosa | Flower |
| HerbaDracocephaliMoldavicae, | Labiatae, Dracocephalum |
Hibiscus trionumapp:addword:Hibiscustrionum |
|||||
| Cane sugar | D(+)-Sucrose | D(+)-Sucrose | |||||
| 37 | Musculoskel etal system (rheumatism) |
Tongzhisurunjia ng Capsules |
Capsule | Y | Colchicum autumnale | Colchicaceae, Colchicum | Capsule |
| ResinaScammoniae | Convovulus scammonial | Gum | |||||
| Stigma Croci. | Iridaceae, Crocus | Stigma | |||||
| Folium Sennae | Leguminosae, senna | Lea | |||||
| FructusChebulae | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||||
| HerbaOperculinaeTurpethi |
Convolvulaceae, Operculina |
Velamen | |||||
| Semen AmygdaliDulcis | Rosaceae, Prunus | Seeds | |||||
| 38 | Musculoskeletal system (rheumatism) |
Compound Luotuopengzi Ointments |
Ointment | Y |
Semen Pegani, Semen HyoscyamiNigeris |
Peganaceae, Peganum Solanaceae, Hyoscyamus |
Seeds Seeds |
| 39 | Nervous system |
Compound Gaoziban Tablets |
Tablet | Y | HerbaAnchusae |
Boraginaceae, Lycopsis,Echium |
Lea |
|
Radix CentaureaRuthenica, |
Asteraceae, Centaurea | Roots | |||||
| Lignum Santali Albi | Santalaceae, Santalum | Roots | |||||
|
Limoniumgmelinii(Wildl.) Kuntze |
Plumbaginaceae, Limonium |
Lea | |||||
| HerbaDracocephali | Labiatae, Dracocephalum |
Hibiscus trionumapp:addword:Hibiscustrionum |
|||||
| Semen LepidiiSativi | Brassicaceae, Lepidium | Seeds | |||||
| FructusPerillaeArgutae | Lamiaceae, Perilla L. | Seeds | |||||
| FlosAnchusae |
Boraginaceae, Lycopsis,Echium |
Flower | |||||
| IncuabulumBombycis | Silkworm cocoon | Silkworm cocoon | |||||
| HerbaLavandulae | Lamiaceae,Lavandula | Flower | |||||
| FructusCoriandri. | Apiaceae, Coriandrum | Seeds | |||||
| 40 | Nervous system |
JianxinHemi'er gaozibanAnbire Tablets |
Tablet | N | HerbaAnchusae |
Boraginaceae, Lycopsis, Echium |
Lea |
| FlosAnchusae, |
Boraginaceae, Lycopsis, Echium |
Flower | |||||
| AmberaGrisea | Ambergris | Bezoar | |||||
| Margarita | Pernulo | Pernulo | |||||
| Succinum | Ambrum | Resin | |||||
| IncuabulumBombycis | Silkworm cocoon | Silkworm cocoon | |||||
| Os Corallii | Agariciidae |
Calcareous skeleton |
|||||
| LignumSantali Albi | Santalaceae, Santalum | Bole | |||||
| AurumFoil | Native gold | Native gold | |||||
| ArgentumFoil | Native silver | Native silver | |||||
| FlosSalixCaprea, etc. | Salicaceae, saliko | Flower | |||||
| 41 | Nervous system |
Xingnaokukeya Tablets |
Tablet | N | Aloe Varae | Liliaceae, Aloe | Lea |
| HerbaAbsinthii | Compositae, artemisia | Lea | |||||
| Mastiche | Burseraceae, Boswellia | Resin | |||||
| ResinaScammoniae | Convovulus scammonial | Gum | |||||
| FructusColocynthis | Cucurbitaceae | Fruit | |||||
| 42 | Nervous system,ophthalmology |
ChuzhangZehai pu Tablets |
Tablet | N | ResinaScammoniae, | Convovulus scammonial | Gum |
| Aloe Varae, | Liliaceae, Aloe | Lea | |||||
| Stigma Croci. | Iridaceae, Crocus | Stigma | |||||
| HerbaOperculinaeTurpeth |
Convolvulaceae, Operculina |
Velamen | |||||
| FructusChebulae | Combretaceae, Terminalia | Fruit | |||||
| FlosRosaeRugosae | Rosaceae, Rosa | Flower | |||||
| Boswelliacarterii | Burseraceae, Boswellia | Resin | |||||
| 43 | Anti-infectious agent |
A'naerFujie Ye | Lotion | Y | CortexGranatii, | Punicaceae, punica | Pericarp |
| FrcutusSophorii | Leguminosae, Sophora | Root | |||||
| FructusCnidii | Umbelliferae, Cnidium | Fruit | |||||
| GallaTurcica, | Gall wasps | Larva | |||||
| OsCorallii | Agariciidae |
Calcareous skeleton |
|||||
| FructusZanthoxyli | Rutaceae, Zanthoxylum | Seeds | |||||
| Borneo |
Dipterocarpaceae, Dryobalanops |
Resin |
Categorized through dosage, the approved TUPMs include about 10 different dosage forms, representatives as 15 in tablets, 7 in granules and 5 in mixture, taking the proportion 34.9%, 16.3% and 11.6% respectively. The only one TUPM injection is Vernonia anthelmintica Injection. Only 8 TUPMs were approved with traditional dosage forms of Uighur medicine, such as liniment, tincture and soft extract. Simultaneously, 20 TUPMs were approved as over-the-counter medicine, with the proportion 46.5% of the total.
Analysis of TUPM patents
Among all the registered TUPMs, 14 TUPMs are related to totally 19 invention patent applications that were mostly submitted after 2000. Consequently 10 TUPMs got patent authorization, mainly focusing on the treatment of skin disease, urogenital disease and respiratory disease. In detail, 5 TUPMs are for skin disease, 2 for urogenital disease and one for each aspect of respiratory, digestive and ophthalmology disease.
Most of these TUPM patents are related to prescription composition. Only the patent of Xi-payimaibizi Liquid involves with quality control and detection and is named “A quality control method to treat prostatitis using traditional Chinese medicine”. The patents of Kaliziran Tincture and Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection are new application patents, named as “Anew use of Kaliziran Tincture to treat or prevent psoriasis” and “A major use of Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection in the data basis of cough-asthma” respectively. Moreover, only Zukamu Granules has got new drug dosage form patent, named as “A preparation and method of cold capsule”. (see Table 2)
Table 2.
TUPM with patent authorization
| No. | Therapeutic areas |
Drug names | Patent names | Patent content type | Application time |
| 1 | Skin disease | Compound Siyadan Tonic | Compound Siyadan Tonic | Prescription | 1995 |
| 2 | Skin disease, cardiovascular disease |
Suziafu Tablets | A preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine composition |
Prescription | 2010 |
| 3 | Skin disease | BaixuanXiatare Tablets | A TCM preparation and method to treat skin disease | Prescription | 2008 |
| 4 | Skin disease | Kaliziran Tincture | A new use of Kaliziran Tincture to treat or prevent psoriasis |
New Application | 2006 |
| 5 | Skin disease |
Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection |
A major use of Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection in the catabasis of cough-asthma |
New Application | 2004 |
| 6 | Urogenital disease |
Xi-payimaibizi Liquid | A quality control method to treat prostatitis using traditional Chinese medicine |
Quality Control | 2010 |
| 7 | Urogenital disease |
KursiKaknaq | Improved traditional patent medicine to treat heat stranguria and ache. |
Prescription | 2005 |
| 8 | Digestive disease |
HuganBuzure Granules | An extraction technology of compound HerbaCichorii |
Prescription | 2009 |
| 9 | Respiratory disease |
Zukamu Granules | A preparation and method of cold capsule | New dosage form | 2002 |
| 10 | Ophthalmology disease |
XuzhangZehaipu Tablets | A preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine to treat cataract |
Prescription | 2008 |
Analysis of TUPM publication
Data analysis of TUPM publications in CNKI showed a steady growth since 2001 to 2011 (see Figure 2). Especially after 2007 there is a rapid increase of paper quantity, implying greater research interest in TUPM.
Figure 2.
Publications of TUPM in CNKI (2001–2011)
Through sorting the number of academic publications, the first ten TUPMCs were summarized in Table 3. Medicines for treating skin disease are still the largest group in number, including Kaliziran Tincture, BaixianXiatare Tablets, Compound MuliZiqi Granules, Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection. The other TUPMs are in the therapeutic areas of urogenital, respiratory, cardiovascular, anti-infection disease and rheumatism. Among all the 408 research articles of TUPM, the maximum quantity appears on the dentistry medicine Xipayi mouth rinse, with 94 academic publications. Xipayimouth rinse is used for sterilization, anti-inflammation, protecting the tooth and oral soft tissues. It's a single-formula preparation with Quercus infectoria Olivas the effective components. It is widely used in Southern Xinjiang Province of China not only by Uighur medicine doctors for treating Abnormal Savda Syndrome but also by ordinary people for self-medication.
Table 3.
Academic publications of ten mostly studied TUPM
| Literature content | ||||||||
| Drug name | Literature quantity | Clinical observation |
Preparation technology |
Quality standard |
Basic research |
Others | ||
| 1 | Xipayi mouth rinse | 94 | 77 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 12 | |
| 2 | Kaliziran Tincture | 91 | 83 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 7 | |
| 3 | BaixuanXiatare Tablets | 43 | 25 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 9 | |
| 4 | Compound Muni Ziqi Granules | 30 | 26 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| 5 | Zukamu Granules | 29 | 5 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 4 | |
| 6 | Aiweixin Liquid | 28 | 11 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 6 | |
| 7 | Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules | 25 | 14 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 4 | |
| 8 | Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection | 24 | 11 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 4 | |
| 9 | Yimusake Tablets | 23 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 3 | |
| 10 | A'naerFujie Ye. | 21 | 0 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 10 | |
| Total | 408 | 258 | 8 | 38 | 44 | 60 | ||
In the respect of research contents, there are 258 clinical observation publications, 63.2% of the total. The rest publications are related to basic researches, quality standard and preparation technology, accounting for 10.8%, 9.3% and 2.0% respectively. In detail, publications about Zukamu Granules and A'naerFujie Ye are highly related to quality standard, and the number of these publications about quality standard accounts for about 30% and 50% respectively. But there is no clinical observation research in the publications of A'naerFujie Ye. In the publications of Aiweixin Liquid, basic research and clinical observation research have nearly the same quantity, each about 34% of the total. (See Table 3)
Analysis of Uighur herb patents
Sorted by the usage frequency in the 43 approved TUPMs, the ten mostly used Uighur herbs can be ordered from high to low as: ResinaScammoniae, Folium FumicisDentati, HerbaDracocephali, Semen AmygdaliDulcis., HerbaChamomillae, FructusPimpinellaeanisi, Cortex Foeniculi, FructusVernoniae, FructusApii, and Radix AnacycliPyrethri.
For patent applications of these ten main Uighur herbs, there are 274 patent applications totally. Among these patent applications, 24 applications have got patent authorizations, with an average authorization rate of 12.4%. The main therapeutic areas of these Uighur herbs include rheumatism, skin disease, urogenital disease and cosmetics (see table 4). Herba Chamomillae has the most patent authorizations, with 13 authorizations from 120 patent applications. Most of its patents focus on the cosmetics area, which are widely used as natural skin care extractions in making hand cream, cleanser and bath cream.
Table 4.
Patent analysis of main Uighur herbs
| Uighur herbs | Plant species | Patent | Main applications | Family of plants | ||
| Total | Authorizations | |||||
| 1 | Folium FumicisDentati |
Rumex dentatus L. |
17 | 2 | Tumor, Cardiovascular Disease | Polygonaceae |
| 2 | Herba Dracocephali |
Dracocephalum moldavica L. |
16 | 0 | Cardiovascular Disease | Lamiaceae |
| 3 | ResinaScammoniae |
Convovulusscammonia L. |
5 | 0 | Rheumatism, Skin Disease and Cataract | Convolvulaceae |
| 4 | Semen AmygdaliDulcis |
Amygdalus communis L. |
4 | 2 | Rheumatism and Urogenital Disease | Rosaceae |
| 5 | HerbaChamomillae |
Matricaria chamomilla L. |
120 | 13 | Cosmetics | Asteraceae |
| 6 | FructusPimpinellaeanisi |
Pimpinel laanisum L. |
0 | 0 | - | Apiaceae |
| 7 | Cortex Foeniculi |
Foeniculum vulgare Mill. |
3 | 0 | Rheumatism | Apiaceae |
| 9 | FructusVernoniae |
Vernonia anthelmintica Willd. |
20 | 5 | Vitiligo and Other Skin Disease | Asteraceae |
| 8 | FructusApii | Apiumgraveolens L. |
7 | 2 | Hypertension, Hyperglycemia, and Rheumatic Diseases Like Arthritis Vitiligo |
Apiaceae |
| 10 | Radix AnacycliPyrethri |
Anacyclus Pyrethrum (L.) DC. |
1 | 0 | Asteraceae | |
The following Uighur herb is FructusVernoniae, with 20 applications and 5 authorizations. These patents are mainly related to the treatment of vitiligo and other skin diseases, except one patent about cough-asthma, which was named as “A major use of Vernonia anthelmintica Injection in remission stage of cough-asthma”.
The mass of patent applications of Folium FumicisDentati concentrate on the extraction technology and preparation process, and half of these patent applications are used to treat tumor and cardiovascular disease. There are two authorized patents involved in two medicines, which were named as “Gandanweifukang Mixture (a medicine for liver and gastrointestinal disease) and its preparation method” and “Abnormal SavdaMunziq and its preparation method” respectively. The patent applications of Semen AmygdaliDulcis are mainly related to the therapeutic areas of rheumatism and urogenital disease, and two authorized patents are “Abnormal SavdaMunziq and its preparation method” and “Improved traditional patent medicine to relieve pain and act as a diuretic”. Furthermore, seven patent applications of FructusApiiare mainly used in the treatment of hypertension, hyperglycemia, and rheumatic diseases, and all of them are about TUM's prescriptions.
The other Uighur herbs' patent applications got no patent authorizations. Herba dracocephali has 16 patent applications, mainly focusing on the research of high flavonoids content, which indicates significant treatment effect towards cardiovascular disease. These patent applications involve some preparations such as sustained release tablets and orally disintegrating tablets of flavones in Herba dracocephali. In addition, FructusPimpinellaeanisi has no patent applications until now.
Analysis of Uighur herb publications
The ten frequently used Uighur herbs have 455 academic publications totally. Among these publications, only 50% are directly related to medicine research. These literatures mostly concentrate on the extraction of the chemical composition and pharmacological activity analysis, accounting about 26.4% of the total publications, followed by clinical effect researches (as shown in Table 5). Meanwhile, the topic concentrations of research literatures are consistent with the patent applications of the Uighur herbs.
Table 5.
Publication analysis of main Uighur herbs
| Herb | Literature quantity | Preparations | Clinical effects | Literature content Component and activity |
Cultivation and planting | Others |
| Resina Scammoniae | 5 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Folium Fumicis Dentati | 33 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 26 |
| HerbaDracocephali | 139 | 10 | 21 | 65 | 10 | 33 |
| Semen AmygdaliDulcis. | 8 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| HerbaChamomillae | 138 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 124 |
| FructusApii | 12 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Radix AnacycliPyrethri | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| FructusVernoniae | 106 | 7 | 44 | 43 | 1 | 11 |
| FructusPimpinellaeanisi | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cortex Foeniculi | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
HerbaDracocephali has the largest amount of research publications, about 139. These researches mainly concentrate on the study of chemical component, including methods of flavonoids determination, HPLC fingerprint and pharmacologic actions of asthmatic rats. In the aspects of clinical effects, studies mainly focus on the influence of coronary heart disease and patients' curative effect observation (Gu et al., 2004; Ren et al., 2011; Song et al., 2010; Tian et al., 2012).
The number of research articles for HerbaChamomillae is about 138, most of which are reports about some cosmetics products. FructusVernoniae has 106 research publications, most of which are medical related, including about 43 chemical component studies and 44 clinical researches.
Especially, clinical effects researches concentrate on the clinical curative effect observation of Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection. Academic publications of Folium FumicisDentatiare are mainly about cultivation, planting and medicinal clinical effects researches. Comparatively, the publications of ResinaScammoniae are less, which are mostly related to TUM preparations, including the quality standard of BaixuanXiatare Tablets and Kukeya Tablets, and the clinical effects of Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules and BaixuanXiatare Tablets. Meanwhile, researches about Semen AmygdaliDulcis are also found to be few: for preparations, there are two research articles including Tongzhisurunjiang Tablets and Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules (Yao, 2012); there are 8 articles about chemical component analysis; and 4 papers about cultivation and planting. Among the 12 research articles of FructusApii, two are involved with the preparations of HanchuanZupa Granules and Ganbaokang Granules.
Radix AnacycliPyrethri has only one research article as well as Cortex Foeniculi, titled as “The quality standard research of TUM preparation Gujingmaisiha Tablets” and “The study of chemical component of Cortex Foeniculi” respectively. In addition, FructusPimpinellaeanisi has no academic publication.
Discussion
Through the analysis of TUM registry, patent and academic publications, this study found that that most of research and development of TUM focus on the therapeutic areas of skin disease, urogenital disease, rheumatism and digestive system disease, implying the medical advantages of TUM in these therapeutic areas.
Publications about the popular Uighur herbs can also validate the effectiveness of those plant species used in the above main therapeutic areas. It is worth noting that researches about the active ingredients of Uighur herbs have been either old or rare (Xu, 1981; Katušin-Ražem et al., 1983; Stahl, 1969). And the researches in recent years focus on the pharmacological activities and the actual clinical application test. Some of plant species are highly considered, such as Herba Dracocephali (Song et al., 2010; Gu et al., 2004; Yang et al., 2013), Fructus Vernoniae (Deng et al., 2002). Those plants have been used for a very long term and still can be used in today with scientific method validated.
Among all the research work about TUM, researches about skin disease account for the largest part, mainly focusing on the treatment of vitiligo and psoriasis. It may have a high relevance to the high morbidity of these two skin diseases in Xinjiang (Wen et al., 2013). Because these skin diseases are significantly influenced by climate, Xinjiang with intense sunlight and arid climate has higher skin disease morbidity (Tang et al., 1998). BaixuanXiatare Tablets, Kaliziran Tincture and Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection are famous medicines used for skin diseases such asvitiligo and psoriasis in Xinjiang, and these medicines are also widely used in Uighur hospitals (Liang, 2011; Liu and Liang, 2012; Wang, 2012;Wei et al., 2009). At present, more attentions are paid on the researches of Kaliziran Tincture and Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection, whose major components are from Uighur herb of VernoniaAnthelmintica L.Vernoniaanthelmintica Injection is a single-formula preparation, also the only injection of TUPM. In particular, some pharmacological researches proved the treatment mechanism of VernoniaAnthelmintica L, showing that VernoniaAnthelmintica L could enhance the activity of tyrosinse and melanin synthesis in A375 cells and increase the tyrosinase mRNA expression, increase melanin synthesis from gene level (Deng et al., 2004; Hui et al., 2010; Ma et al., 2008).
Although there are quite a few species of TUM related to urogenital disease, few researches and patent authorizations are carried out until now. The main Uighur patent medicines related to urogenital disease are Xi-payimazibizi Liquid treating prostatitis and KursiKaknaqused for urinary tract infection. They also have significant component differentia. For the reason of less research articles about the two TPUM, except for a few clinical observation researches, the knowledge about their function mechanism and the effective chemical composition is rare.
Rheumatism belongs to musculoskeletal disease in the ATC classification system. Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules is the most famous anti-rheumatism medicine in Xinjiang. Evidences form pharmacological and clinical study show that Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules can relieve the symptom of acute gouty arthritis patients effectively and promptly (Fan et al., 2009; Zhu et al., 2013), reduce the ESR and c-reactive protein, and also suppress expression of IL-1β, TNF-α in serum. It's proved to be an effective way to treat the acute gouty arthritis (Yao, 2012).
At last, this study showed there are several TUPMs for treating digestive system disease. However, only HuganBuzure Granules got patent authorization. This medicine is aiming at the treatment of stomachache, cirrhosis, hepatitis and other diseases, with few research articles and clinical efficacy evidence. Additionally, extractions of HuganBuzure Granules have protective effect on liver injury in mice (Wu et al., 2011).
HerbaDracocephali, FructusVernoniae, HerbaChamomillaeand FoliumFumicisDentati have been mostly studied Uighur herbs. Most of literatures on HerbaDracocephali focus on the content of flavonoids compounds and pharmacological activity (Yan et al., 2003). The studies show that the flavones of HerbaDracocephali could inhibit the proliferation of VSMC induced by TNF-α, which might be one of the pharmacological mechanisms of HerbaDracocephali total flavoes in treatment for atherosclerosis (Cao et al., 2011; Song et al., 2010). In clinical curative effect, there is less study on HerbaDracocephali. FructusVernoniae is the major components of pharmaceutical preparation in treating psoriasis and vitiligo, and major research is conducted on chemical composition and extraction technology (Yao, 2007; Yu et al., 2007). HerbaChamomillaehas protective effect to skin and it is widely used in cosmetics for research has shown the anti-inflammatory effect of volatile oil from it (Yuan et al., 2011). The study of Folium FumicisDentati is mainly on the extraction process of flavonoids. However there is no research on pharmacological action and clinical effect (Nurma-mmat et et al., 2008; Palida et al., 2013).
In general, while the curative effect of TUM has been proved to some degree, lacks of using modern technologies may cause uncertain effect, which has affected the standardization of TUM. The shortage of applying modern technologies has limited TUM in drug-approval and medical application.
Conclusion
As a part of China and Central Asia's traditional medicine, TUM in Xinjiang play an important role in the local care system, at the same time, it promotes the cross-regional communication and development of health. This study finds that the TUM in Xinjiang has a vital value and abundant experience in treatment of skin disease, urogenital system disease, rheumatism and respiratory system disease. On the one hand, this study can provide some new ideas and methods for these diseases' treatment, especially for patients with some intractable diseases such as psoriasis and vitiligo. On the other hand, traditional Uighur herbs can be a reservoir of traditional medicinal plants with potential for the development of some diseases' modern therapeutics. These traditional Uighur herbs with excellent curative effect should be screened in detail for their phytochemical properties and pharmacological activity to discover new bioactive constituents, then provide knowledge base for new drug's R&D. Further, more studies for TUM should be carried out, and the efficacy and safety of TUM should be evaluated for pharmacological studies especially the species with high value.
Table 6.
Contents of publications
| Herb | Component and activity literature quantity |
Phytochemical constituents | Published pharmacological activity reports |
| Resina Scammoniae | 0 | Scammoniae resina | No |
| Folium Fumicis Dentati | 1 | Chrysophanol, Emodin, Aloe-emodin, Physcion, Phytosterol, Phytosterol ester, Free Fatty Acid |
Research on the active ingredients of hemostasis (Xu, 1981) |
| Herba Dracocephali | 65 | Sorbarin, Scutellarein Rhamnoside, Linarin |
Review research of chemical component and pharmacological activity (Song et al., 2010); research on the chemical component of Herba Dracocephali (Gu et al., 2004); chemical constituents and their pharmacological activities research (Yang et al., 2013), etc. |
| Semen Amygdali Dulcis. | 1 | Vegetable oil, Protei, Starch, Vitamin A, B1, B2, Digestive Enzyme |
No |
| HerbaChamomillae | 8 | ChaPaxulene, Proazulere, Farnesene, Bisabolol, A-bisabolol Oxide-A, Suaianolide, Matrioin, Matricarin |
Radiation treatment of herb tea for the reduction of microbial contamination (Flores chamomillae) (Katušin-Ražem et al.,1983), etc. Thin layer chromatography for characterization of pharmacopeia drugs (Stahl,1969), etc. |
| Fructus Apii | 1 | Eucalyptol, Umbrella Lactone, Celery Element, Linolenic Acid, Volatile Oil, Flavonoids, Boron, Minerals |
No |
| Radix Anacycli Pyrethri | 0 | Volatile Oil: | No |
| Caryophyllene, β-pinene, | |||
| Ethybutylether | |||
| Fructus Vernoniae | 43 | Volatile Oil | Explore the effect of the Vernoniaanthelmintica wild Injection on the lymphocyte subclass of mice (Deng et al., 2002). The content of flavonoids in the fruit and various medical forms of fructus vernonia is tested by spectrophotometry (Zhou et al., 2000), etc. |
| Fructus Pimpinell aeanisi | 0 | Anisole | No |
| Cortex Foeniculi | 1 | Fennel essential oil, Polysaccharide, Anethole |
Investigate the in vitro anti-candidal activity of the essential oil of Illicium verum (EOIV) alone and in combination with fluconazole. (Zhao et al., 2004), etc. |
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the research funding of University of Macau MYRG160(Y2-L2)-ICMS11-HH).
References
- 1.Amat N, Upur H, Ablimit A, Matsidik A. Immunomodulatory effects of Abnormal Savda Munsiq, a traditional Uighur medicine, on the combined stress mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2009;122:42–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2008.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cao WJ, Xing JG, Wang XC, Jin JG. Inhibitory Effects of Dracocephalum Total Flavoes on Proliferation of Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Induced by TNF-α. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. 2011;17:159–162. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Deng RC, Zhou Y, Zhang WS, Xu JG. Study on mechanism of therapy of vitiligo by Vernonia anthelmintica willd. Letters in Biotechnology. 2004;15:573–577. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fan P, Yang R, Hua L. Curative effect of Tongzhisurunjiang Capsule on 48 gouty arthritis cases. Chinese Jouranl of Traditional Medical Traumotology & Orthopedics. 2009;17:43–44. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Geng DS. The medical theories and the researching developments of the medicinal herbs in Uygur. Journal of Medicine & Pharmacy of Chinese Minorities. 2006;13:5–7. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gu HF, Chen RY, Sun YH, Liu F. Studies on chemical constituents from herb of Dracocephalum moldavica. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2004;29:232–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hui HY, Zhang CF, Wu N, Li QR, Sun XY. Effects of Vernonia anthelmintica Willd combined NB-UVB irradiation on the expression of c-KIT and PAR-2 Protein in mice epidermis. Diagnosis and Therapy Journal of Dermato-Venereology. 2010;24:814–818. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Katušin-Ražem B, Ražem D, Dvornik I. Radiation treatment of herb tea for the reduction of microbial contamination (Flores chamomillae) Radiation Physics and Chemistry. 1983;22(3):707–713. 1977. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liang GY. The clinical observation on Kaliziran Tincture combined with Vernohia anthelmintica Willd Injection in vitiligo. China Medical Abstract of Dermatology. 2011;28:211–212. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu ZJ, Liang L. Effect observation of the union treatment with Baixuan Xiatare Tablets and Acitretin Capsules on vulgaris psoriasis. Guide of China Medicine. 2012;10:197–199. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ma HJ, Zi SX, Li Y, Liu W, Wang YX. The effect of Vernonia anthelmintica flavone on melanogenesis of human melanocytes in vitro. Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine. 2008;17:524–526. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nurma-mmat M, Yang WL, Amar T, Na-sir G. Study on extraction process of total flavonoids in Anchusa italica Retiz. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research. 2008;19:1303–1304. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Palida A, Cong Y, Ya M, Bai T. Optimization of ultrasound extraction process of total flavonoids from Anchusa italica by response surface methodology. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. 2013;19:48–52. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ren WD, Xing JG, Wang XC, Xue GP. Preparation and influencing factors on release of total Dracocephalum moldevica flavonoids osmotic pump tablets. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. 2011;17:13–17. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Song R, Jin CS, Zhou YW. To determine content of total flavonoids and Robinin-7-o-β-D-xylosylglucoside from Dracoephalum mololarie. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae. 2010;16:71–75. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stahl E. Thin layer chromatography for characterization of pharmacopeia drugs. 5. Chamomile flowers flores Chamomillae. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 1969;19(11):1892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tian YQ, Shang J, He T, Cai WY. Study on material basis of Dracocephalum moldavica for protecting cardiomyocyte against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by traditional Chinese medicine serum chemical and pharmacological methods. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2012;37:620–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tang ZL, Peng YN, Shao CG, Zhou XL. A correlation study of incidence of psoriasis and meteorological factors. Chinese Journal of Dermatology. 1998;31:75–77. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Upur H, Yusup A, Baudrimont I, Umar A, Berke B, Yimit D, Lapham J C. Inhibition of cell growth and cellular protein, DNA and RNA synthesis in Human Hepatoma (HepG2) cells by ethanol extract of Abnormal Savda Munziq of traditional Uighur medicine. Evidence Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2011;25:14–24. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nen062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang JT. Effect observation of the union treatment with NB-UVB and Baixuan Xiatare tablet on vulgaris psoriasis. Diagnosis and Therapy Journal of Dermato-Venereology. 2012;19:294–297. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang YZ, Lv FM, Han YM. Introduction of Uighur medicine's resource and theory. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2005;30:316–317. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wei KK, Hu BS, Gao YJ. The effect observation on Fufang Kaliziran Tincture combined with Vernohia anthelmintica Willd Injection in vitiligo. Journal of Medical Forum. 2009;30:94–95. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wen Q, Chen JY, Liu HX. Geographical feature and treatment strategy of psoriasis's formation. Xinjiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2013;31:3–4. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wu T, Jiang L, Aisa H, Sun YH. Study on new extraction technology and protective effect of Hugan Buzure Granules on liver injury in mice. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2011;36:429–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu ZW. The research on the chemical component of Anchusa. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 1981;2:79–80. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yan LL, Kang XL, He CH. Effects of moldavica total flavone on regulation of Th1/Th2 imbalance in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic rats. Journal of China Medical University. 2013;42:142–145. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yang LN, Xing JG, He CH, Yang PM. Chemical constituents of Dracocephalum moldavica L. and their pharmacological Activities. World Clinical Drugs. 2013;34(4):226–231. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yao L. Experimental study of the correlation between different extraction methods and functional mechanisms of Vernonia anthelmintica. Xinjiang Medical University; 2007. Master Thesis. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yao YT. The tablet of Tongzhisurunjian study on the Preparation and quality standard. Wuhan University of Technology; 2012. Master Thesis. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yuan Y, Long ZJ, Yang JJ, Yuan CH. Study on the anti-inflammatory effect of volatile oil from Matricaria Chamomilla L. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. 2011;18:52–55. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yu LH, Sun L, Li YJ, Shang J. Study on extraction techniques for Vernonia anthelmintica by grading methods. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy. 2007;5:373–375. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhao J, Luo Z, Wu S. In vitro anti-candidal activity of the essential oil of Illicium verum. Chinese Journal of Dermatology. 2004;37(8):475–477. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhou XY, Hu XJ, Tian SG, Zhou ZC. Research on Chemical Component of the Fruit and Various Medical Forms of Uigurian Medicine Fructus Vernonia. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy. 2000;2:023. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhu L, Ying W, Yi Z. The effect of Tongzhisurunjiang Capsules to treat gouty arthritis. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine. 2013;9:171–172. [Google Scholar]