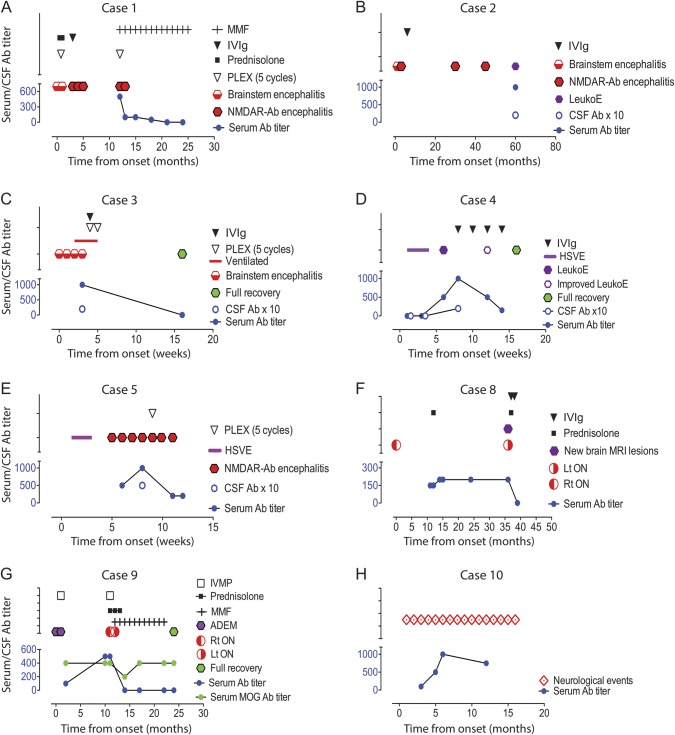
Figure 2. NMDAR-Ab levels, clinical syndromes, and therapy in 8 informative patients with white matter syndromes in association with NMDAR-Ab.
(A–C) Cases 1–3 presented initially with brainstem encephalitis; Cases 1 and 2 relapsed with encephalopathy, psychiatric features, movement disorder, and dysautonomia. Case 2 had additional seizures. In both, the diagnosis of NMDAR-Ab encephalitis was made at the time of relapse. Case 3 had a monophasic illness and did not have any of the clinical characteristics of NMDAR-Ab encephalitis. (D, E) Cases 4 and 5 presented with herpes simplex virus encephalitis (HSVE) and then had a neurologic relapse, which correlated with raised NMDAR-Abs in both serum and CSF and demonstrated a clinical response to immunotherapy with reduction of antibody levels. (F) Case 8 presented with optic neuritis and poor visual recovery, which prompted a neuroinflammatory screen and the identification of the antibody positivity. She only received a course of steroids 1 year into her illness and 3 years later had a neurologic relapse. (G) Case 9 presented initially with 2 episodes of acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM) and relapsed at 1 year with optic neuritis. He was also MOG-Ab positive, which remain detectable even when NMDAR-Abs are no longer detectable and when the patient had clinically recovered. (H) Case 10 had recurrent episodes of hyperventilation, dizziness, and double vision; did not receive any treatment; and both her clinical and radiologic features remained unchanged. Ab = antibody; CSF Ab × 10 = NMDAR antibody titers in CSF (all between 1:20 and 1:50) multiplied by 10 to provide visibility in comparison to serum levels; IVIg = IV immunoglobulin; IVMP = IV methylprednisolone; LeukoE = radiologic leukoencephalopathy; Lt = left; MMF = mycophenolate mofetil; NMDAR = NMDA receptor; ON = optic neuritis; PLEX = plasma exchange; Rt = right; Serum Ab titer = titer measured by endpoint dilution.