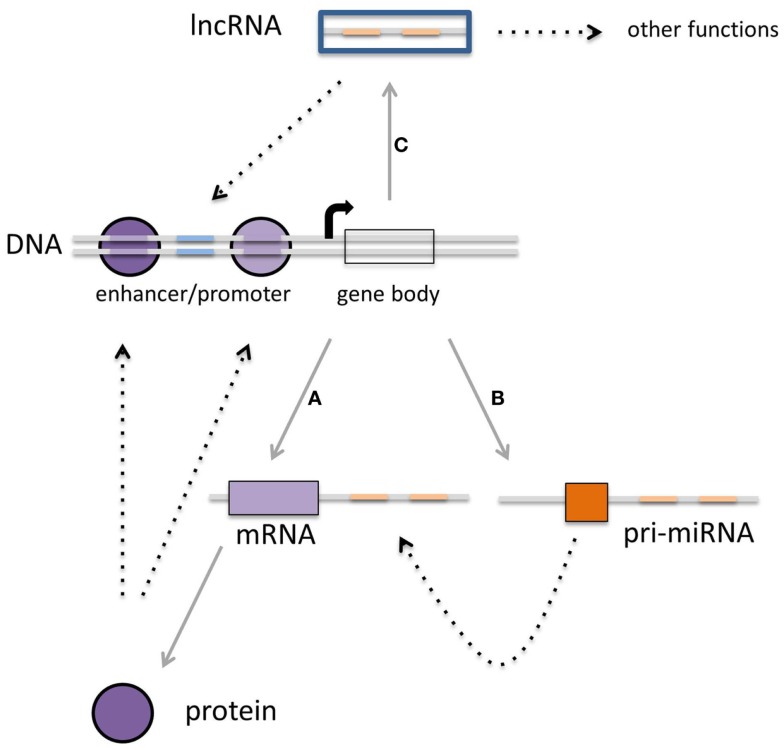
Figure 1.
Multiple layers of gene expression controlled by transcription factors, miRNAs, and lncRNAs. (A) Protein-coding genes are transcribed into mRNA, which subsequently are translated into proteins. These proteins can function as the classical transcription factors. (B) There is a second class of RNAs that is not translated into protein but rather is regulating the expression of other transcripts. The third class of transcripts described in this review (C) is the long non-coding RNAs that can regulate gene expression as well, although other functions for these transcripts have been described (see Figure 3). It is becoming clear that there is interaction within each class, but also between these three classes, which can converge on transcriptional outcome (see text for details).