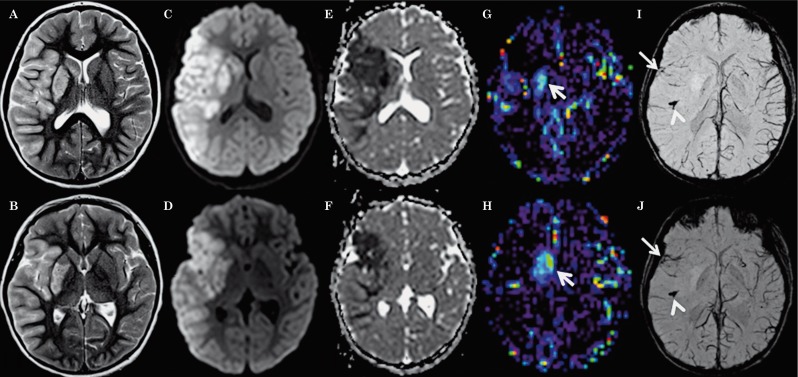
Figure 1.
Axial T2-weighted (A,B), trace of diffusion (C,D), ADC maps (E,F), CBF-ASL maps (G,H) and minIP-SWI images (I,J) 8 hours after onset of symptoms show T2 hyperintense signal abnormalities and restricted diffusion (hyperintense signal abnormality on C,D with matching low ADC values on E,F) involving the cortex as well as subcortical and deep white matter within the right MCA territory as well as right putamen and caudate nucleus. Restricted diffusion in the anterior tip of the right temporal lobe and insula matches the territory drained by SWI hypointense sulcal veins (arrows on I,J). The rest of the right MCA territory appears less affected on ADC maps and the sulcal veins draining this territory appear less prominent and especially less SWI hypointense suggesting lower oxygen extraction fraction. In these parts of the right MCA territory, CBF-ASL maps appear symmetrical to the contralateral MCA territory suggesting relative normal perfusion. The veins draining the right anterior basal ganglia are less SWI hypointense matching increased absolute CBF on the ASL map demonstrating hyperperfusion (arrows on G,H). Additionally, the minIP SWI images demonstrate thrombus in the M2 segment of the right MCA with susceptibility artifacts along the course of the vessel (arrowheads in I,J).