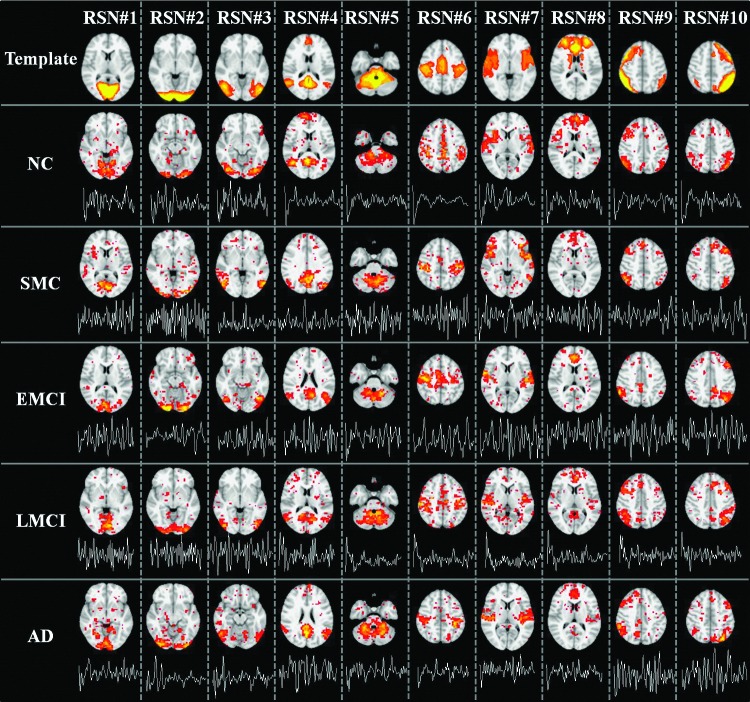
FIG. 2.
Ten well-matched RSNs identified from sparse representation. The first row showed the 10 RSN templates. For each template, the most informative slice, which is superimposed on the MNI152 template image, was shown as the spatial pattern. Rows 2 to 6 show the identified RSNs of a randomly selected subject of five groups (NC, SMC, EMCI, LMCI, and AD), respectively. In each subfigure, the most informative slice, superimposed on the MNI152 template image, was shown as the spatial pattern of a specific RSN. The time series of corresponding atom was also shown below each spatial pattern of the RSN. All 10 RSNs were matched by calculating and sorting the overlapping rate with the corresponding RSN templates (first row) provided in http://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/analysis/brainmap+rsns/ (Smith et al., 2009). The RSN templates shown in first row were thresholded at z=3. The color scale of spatial maps in sparse representation ranges from 0.1 to 10. AD, Alzheimer's disease; EMCI, early mild cognitive impairment; LMCI, late mild cognitive impairment; SMC, significant memory concern. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/brain