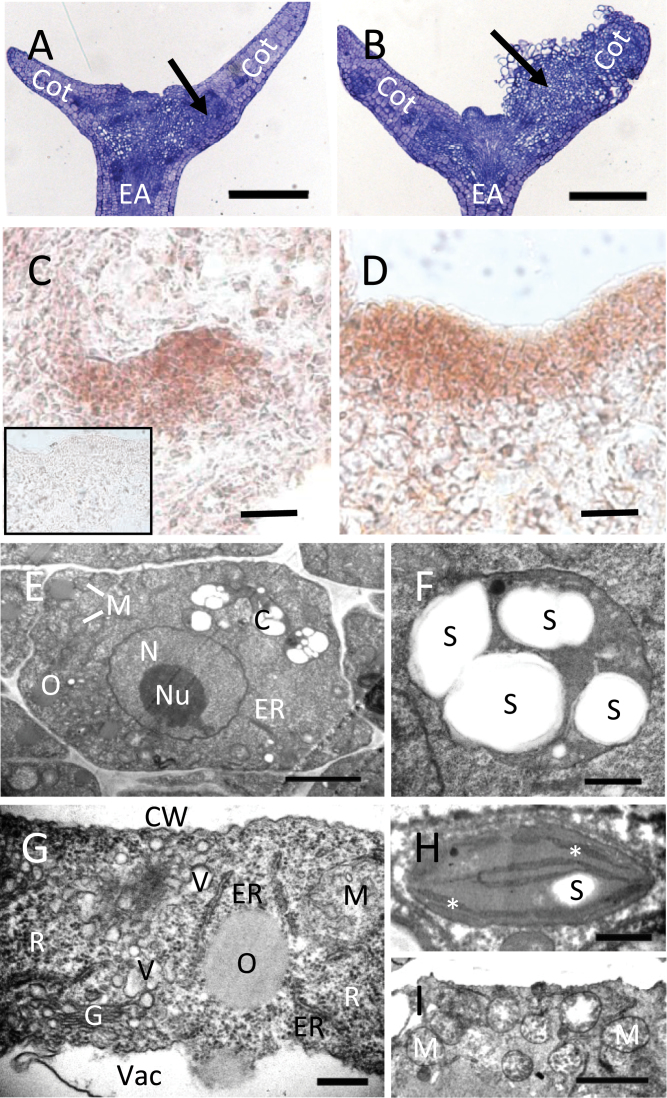
Fig. 3.
Structural features of WT and vtc2 tissues during SE. (A, B) Medial longitudinal sections of a explants at D7I (+2,4-D) showing cell division within the cotyledon. EA, embryo axis; Cot, cotyledon. Arrows show areas of callus initiation. Bars, 250 µm. (A) WT embryo with evidence of some cell division in the cotyledon. (B) In vtc2-5, tissues were re-organizing and beginning to develop callus in the cotyledon. (C, D) In situ hybridization of SHOOTMERISTEMLESS in proliferating tissue at D7I in WT (C) and vtc2-5 (D) using an anti-STM probe (sense probe, inset). Bars, 20 µm. (E–I) TEM images of WT versus vtc2 somatic embryos during induction. (E) A typical whole cell from a WT somatic embryo. Note the lack of mitochondria and endomembrane system relative to vtc2. N, nucleus; Nu, nucleolus; M, mitochondria; O, oil body; C, chloroplast; ER, endoplasmic reticulum. Bar, 2 µm. (F) A chloroplast from a WT SE showing multiple starch granules (S). Bar, 500nm. (G) Extensive endomembranous structures and ribosomes (R) are found in the cytoplasm of a vtc2 somatic embryo cell. G, Golgi; V, vesicle; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; M, mitochondria; O, oil body; CW, cell wall; V, vacuole. Bar, 300nm. (H) A chloroplast from a vtc2 somatic embryo. Starch (S) is rare and smaller than in the WT. Thylakoid membranes are indicated by an asterisk. Bar, 500nm. (I) Many mitochondria (M) in the cytoplasm of a vtc2 somatic embryo cell. Bar, 2 µm. (This figure is available in colour at JXB online.)