Fig. 2.
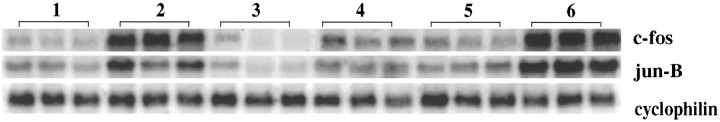
Chronic amphetamine-induced downregulation of IEG mRNA in vivo is blocked by MK-801 pretreatment. Northern blots of rat striatal mRNA probed with c-fos andjun-B. Rats were treated for 12 d as summarized in Table 1. Lane 1 represents the control condition; lane 2, the acute amphetamine condition; lane 3, chronic MK-801 condition; lane 4, chronic amphetamine administration (4 mg/kg); lane 5, chronic amphetamine administration preceded by MK-801 pretreatment with each dose; and lane 6, chronic amphetamine condition preceded by MK-801 pretreatment for 11 d with MK-801 pretreatment replaced by saline on day 12. Acute treatment with amphetamine (4 mg/kg) leads to a marked induction of IEGs (lane 2); chronic amphetamine administration (lane 4) leads to a reduced response. This downregulation of IEG inducibility is blocked by pretreatment with MK-801 before amphetamine injections, i.e., when MK-801 is omitted at the last injection, the response to amphetamine (lane 6) is similar to the acute, indeed greater (lane 2), rather than the chronic (lane 4), amphetamine condition. Rats were killed 30 min after the last injection. Cyclophilin was used as internal loading control; n = 6.