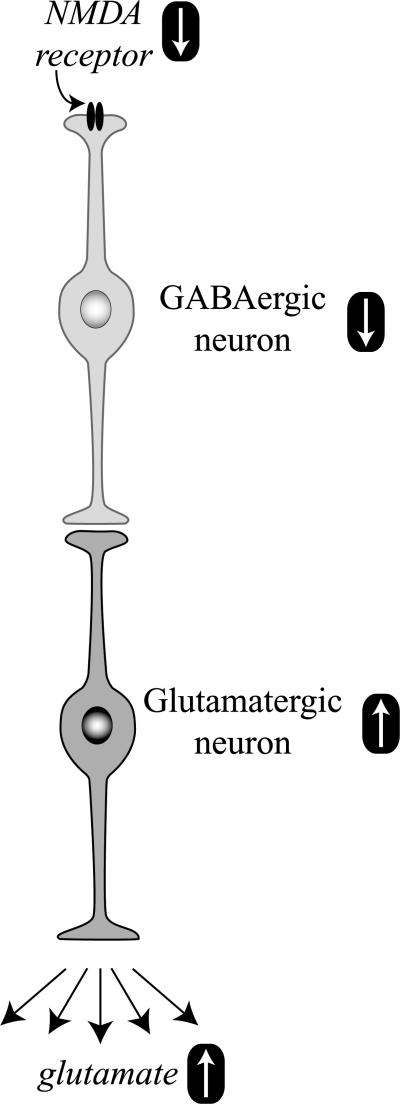
Fig. 6.
NMDA receptor hypoactivity and glutamate neurotoxicity. Hypoactive NMDA receptors on GABAergic neurons are responsible for decreased neuronal activity. The inhibitory tone of GABA neurons on glutamate neurons is attenuated, and the activity of glutamate neurons is increased. More glutamate gets released, causing excitotoxic stress and damage.