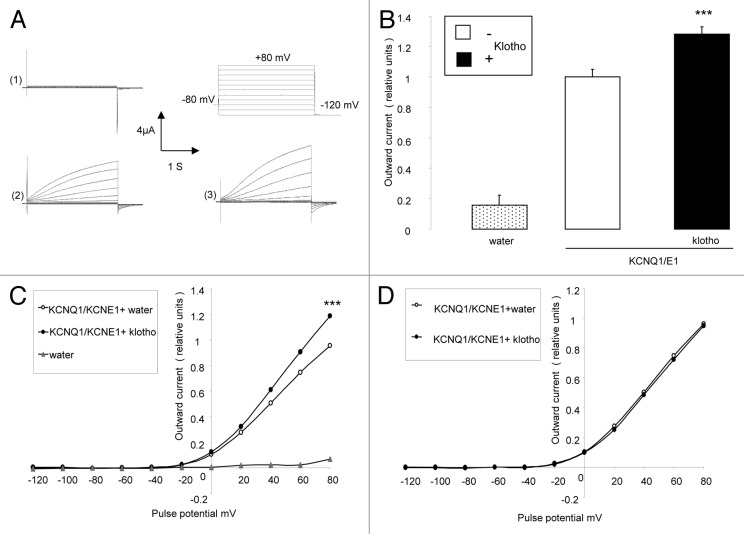
Figure 1. Effect of Klotho coexpression on current in KCNQ1/KCNE1 expressing Xenopus oocytes. (A) Original tracings demonstrating outward K+ currents activated by depolarization from -120 to +80 mV in 20 mV steps from a holding potential of -80 mV in Xenopus oocytes injected with water (1), injected with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 (2) and in Xenopus oocytes injected with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Klotho (3). (B) Arithmetic means ± SEM (n = 16–57) of the normalized depolarization-induced K+ current at +80 mV in Xenopus oocytes injected with water (dotted bar), with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1(white bar) or with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Klotho (black bar). *** indicates statistically significant (P < 0.001) difference of KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Klotho expressing Xenopus oocytes from Xenopus oocytes expressing KCNQ1/KCNE1 alone. (C) Arithmetic means ± SEM (n = 16–57) of the normalized depolarization-induced K+ current as a function of voltage in Xenopus oocytes injected with water (gray triangles), with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 (white circles) or with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Klotho (black circles). *** indicates statistically significant (P < 0.001) difference of KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Klotho expressing Xenopus oocytes from Xenopus oocytes expressing KCNQ1/KCNE1 alone. (D) Arithmetic means ± SEM (n = 56–57) of the normalized depolarization-induced K+ current to the maximum peak current of each respective group as a function of voltage in Xenopus oocytes injected with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 (white circles) or with cRNA encoding KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Klotho (black circles).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.