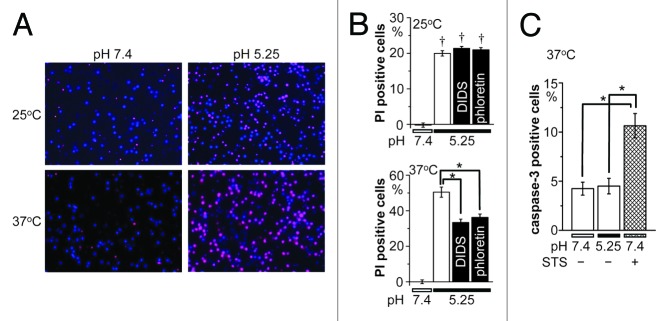
Figure 4. Acidotoxic necrotic death of cortical neurons and its sensitivity to hypothermia and anion channel blockers. (A) Representative fluorescence micrographs of cortical neurons stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue) for nuclei of all neurons and with PI for nuclei of injured neurons 1 h after exposure to control (pH 7.4) or acidic (pH 5.25) solution at 25 or 37 °C. (B) Summarized data showing the fraction of PI-positive neurons at 25 °C (top) and 37 °C (bottom) in neutral pH or acidic solution in the absence or presence of 10 μM DIDS or 50 μM phloretin. (C) Caspase-3 activity after exposure to control (pH 7.4) or acidic (pH 5.25) solution for 1 h at 37 °C in the absence or presence of 0.5 μM STS. Each column represents the mean (with the SEM bar) of 28−96 (B) or 5−10 (C) samples. Daggers indicate significant differences (P < 0.01) between the data obtained at 25 and 37 °C (B). Single asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.01) between the data obtained at 37 °C without and with anion channel blockers (B) or between those in the presence and absence of STS (C).
