Figure 4. Kctd12 mutation causes a decrease in thigmotactic behavior.
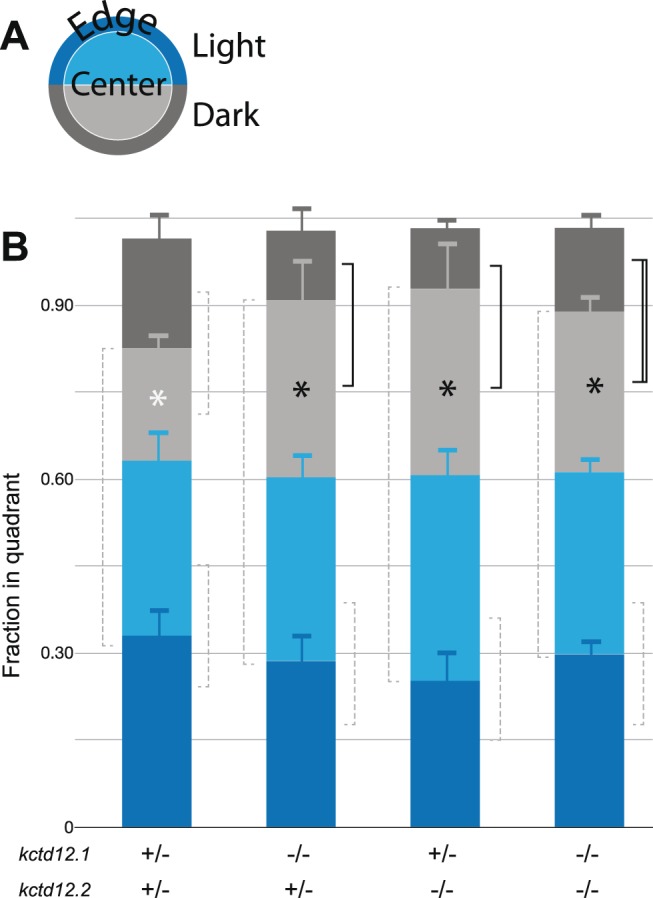
A. Each well of a 6-well plate is divided into halves with dark (gray) or clear (blue) bottoms. The well is further divided into center (light) and edge (dark). The position of the fish is recorded every half second to measure scototaxis or thigmotaxis. The center is defined as 60% of the area of the circle (inner) and the edge as the remaining 40% (outer). Double heterozygous larvae were used as controls B. Scototaxis. No change in scototaxis is detected between genotypes. All genotypes prefer the light. Dotted lines are ns. Thigmotaxis. Preference for the center increases in Kctd12 single and double mutants (solid line: p<0.05, double line: p<0.01, 2-tailed t-test). Pooling mutant animals for a comparison to double heterozygote controls showed a significant effect of genotype (white vs. black * p<0.01). kctd12.1/2+/− n = 19; kctd12.1/2−/− n = 9; kctd12.1−/−, kctd12.2+/− n = 11; kctd12.1+/−, kctd12.2−/− n = 7.
