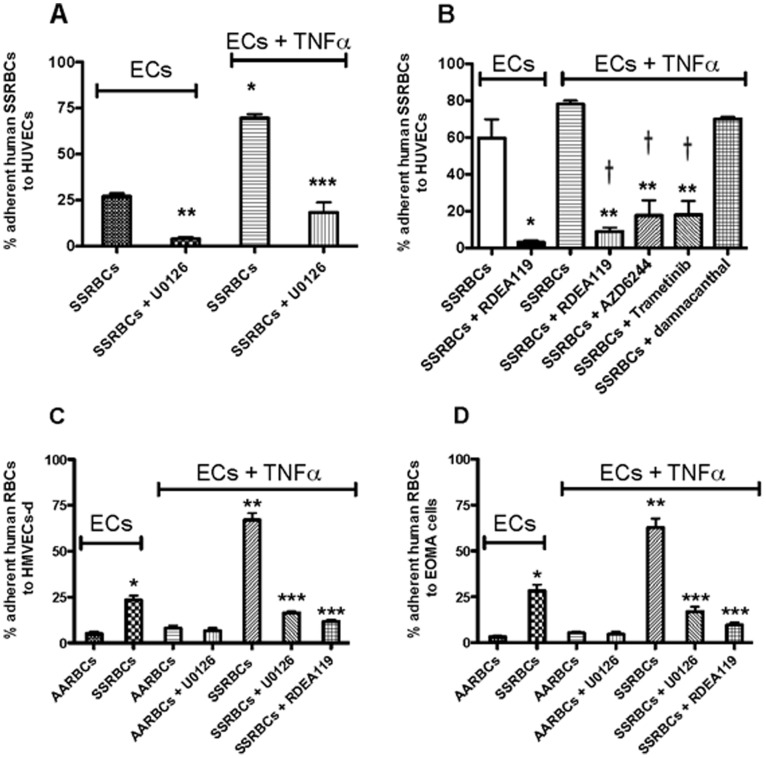
Figure 1. MEK inhibition down-regulates SSRBC adhesion to both non-activated and activated endothelial cells in vitro.
The effects of MEK inhibitors on SSRBC adhesion to HUVECs, HMVECs-d and EOMA cells was tested in intermittent flow condition assays at different shear stresses in vitro. Results are presented as % adherent SSRBCs at a shear stress of 2 dynes/cm2. A. SSRBCs were sham-treated or treated with 100 nM MEK inhibitor U0126 prior to adhesion assays to non-treated and TNFα-treated HUVECs. *: p<0.0001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to non-treated HUVECs; **: p<0.001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to non-treated HUVECs; ***: p<0.0001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to TNFα-treated HUVECs. Error bars show standard error mean (SEM) of 4 different experiments. B. SSRBCs were sham-treated, or treated with 100 nM RDEA119, 100 nM AZD6244, 100 nM trametinib, or 10 µM damnacanthal prior to adhesion assays to non-treated and TNFα-treated HUVECs. *: p<0.0001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to non-treated HUVECs; **: p<0.0001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to TNFα-treated HUVECs; and †: p<0.001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to non-treated HUVECs. Error bars show SEM of 3 different experiments. C–D. SSRBCs and normal RBCs (AARBCs) were sham-treated, or treated with 100 nM U0126 or 100 nM RDEA119 prior to adhesion assays to non-treated and TNFα-treated HMVECs-d (C) and EOMA cells (D). *: p<0.0001 compared to sham-treated AARBCs adherent to non-treated HMVECs-d (C) and EOMA cells (D); **: p<0.0001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to non-treated HMVECs-d (C) and EOMA cells (D); and ***: p<0.001 compared to sham-treated SSRBCs adherent to TNFα-treated HMVECs-d (C) and EOMA cells (D). Error bars show SEM of 3 different experiments for C and D.