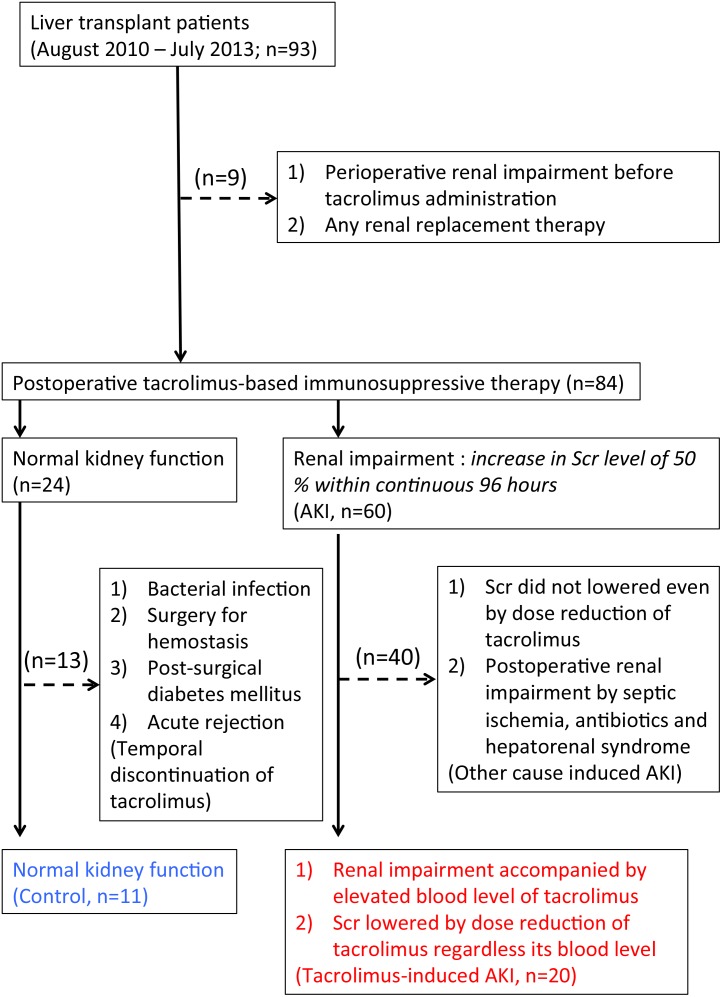
Figure 1. Diagnostic algorithm of tacrolimus-induced AKI in the patients after liver transplantation.
Between August 2010 and July 2013, 93 patients were enrolled with the written informed consent. Nine patients with perioperative renal impairment before the administration of tacrolimus-based posttransplant immunosuppressive treatment and patients with any renal replacement therapy were excluded. Patients with renal impairment by some other causes including septic ischemia, antibiotics and hepatorenal syndrome were also excluded from this study. In addition, the patients of renal impairment with low tacrolimus levels, whose Scr levels were not changed even by the decrease of tacrolimus dosage, were also excluded indicating other causes-derived renal impairment such as tubular necrosis post-surgery. Among 24 patients with normal kidney function, 13 patients with post-transplant infectious disease, surgery for hemostasis, post-surgical diabetes mellitus and acute rejection episode were excluded for the temporal discontinuation of tacrolimus administration. Finally, the clinical data of the 11 control patients and 20 patients with tacrolimus-induced AKI were used.