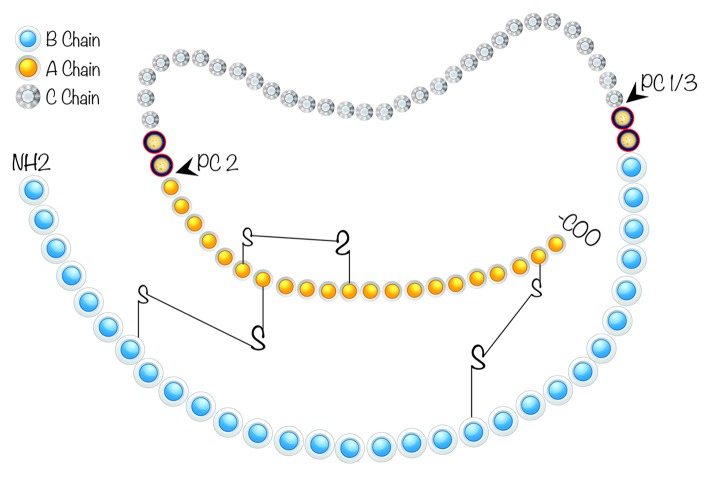
Figure 1. Schematic representation of human proinsulin. C-peptide, a 31 amino acid (aa) residue peptide, is depicted between A (21 aa) and B (30 aa) chains. In healthy individuals, both insulin and C-peptide are secreted in equimolar amounts from pancreatic β cells. In patients with diabetes, pancreatic β cells are destroyed by auto-immunity resulting in deficiency of both insulin and C-peptide. Although diabetic patients may routinely receive insulin injections to compensate the insulin deficit, no replacement for C-Peptide is currently administered to diabetic patients. Prohormone Convertase (PC 1/3 and PC 2) cleavage sites necessary for the removal of C-peptide from insulin are also shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.