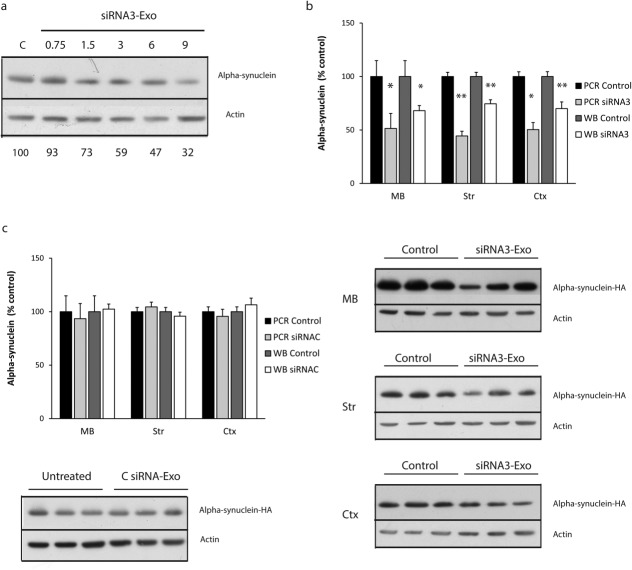
FIG 4. Down-regulation of human S129D α-Syn in SHSY5Y cells and Tg13 mice using siRNA3 RVG-exosomes.
(A) Western blot analysis of α-Syn-HA levels relative to actin 3 days after the addition of increasing amounts of siRNA3-RVG exosomes (0.75-9 µg exosome protein) to SH-SY5Y cells expressing human S129D α-Syn-HA; lower numbers represent α-Syn protein level relative to actin. (B) qPCR and Western blot analyses of human S129D α-Syn-HA expression in various brain regions from Tg13 mice (5 months of age) 7 days after intravenous injection with 150 μg siRNA3 RVG-exosomes (siRNA3), and compared with untreated controls (con). Mid brain (MB), striatum (Str), and cortex (Ctx) samples analyzed for S129D α-Syn-HA mRNA levels (PCR siRNA3) were expressed relative to GAPDH mRNA and S129D α-Syn-HA protein levels (anti-HA antibody) expressed relative to actin levels (WB siRNA3). Data were normalized to brain regions from matched controls (PCR control, WB control). Typical blots of the midbrain, striatum, and cortex samples are shown. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 8). Statistical analyses compared with control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. (bold>C) As a control, Tg13 mice were injected with 150 μg CsiRNA RVG-exosomes (loaded with the control siRNA) and compared with untreated controls (control). Seven days after injection, brains were dissected (n = 8 per region) and analyzed as described in section B. A Western blot of the midbrain samples is shown.