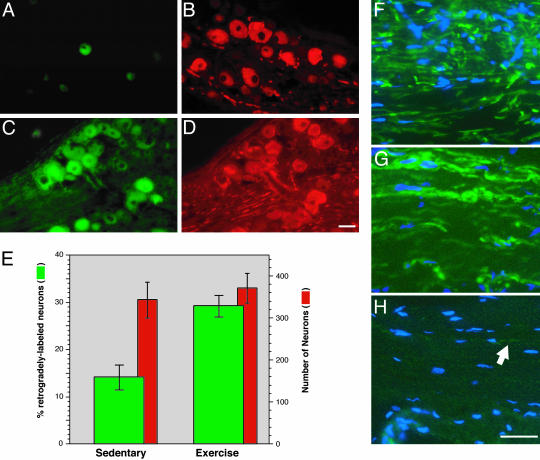
Fig. 3.
Exercise-conditioned animals show increased nerve regeneration after crush injury. Sedentary and 7-day-exercised animals were subjected to sciatic nerve crush. Three days after crush, the nerve was transected at 8 mm distal to the crush site and was exposed to FluoroGold for additional 2 days. FluoroGold-positive neurons were more abundant in the L4–5 DRGs from the exercised animals (B) than in those from the sedentary animals (A). Costaining for neurofilament antibody showed similar numbers of neurons in these sections (C and D). Mean number of retrogradedly labeled neurons (FluoroGold-positive, left axis) and total neurons (neurofilament-positive, right axis) are presented of three serial sections from three animals for each condition in E (error bars = SD). (G and H) Representative sections of sciatic nerve distal to the crush site that were stained for neurofilament (green) and counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue). Sections of uninjured sciatic nerve taken at a distal thigh level are shown for comparison (F). Only a few axons were discernable in the sections of crushed nerve from the sedentary animals (arrow, H). (Scale bars: 50 μmin A–D and 20 μmin F–H).