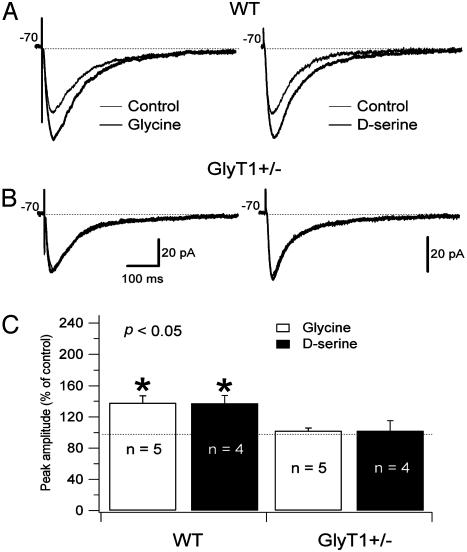
Fig. 3.
Administration of 10 μM glycine and 10 μM d-serine increase the amplitude of the evoked NMDAR currents of pyramidal cells in WT mice but not in GlyT1(+/-) mice. Pyramidal cells were recorded in a low Mg2+ ACSF (0.1 mM) in the presence of 2,3-dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoylbenzo[f]quinoxaline (NBQX) (20 μM), picrotoxin (50 μM), CGP 52432 (10 μM), and strychnine (0.5 μM). Responses were evoked by bipolar electrical stimuli at Vm = -70 mV in pyramidal cells of WT (A) and GlyT1(+/-) (B) mice. The NMDAR currents recorded in low Mg2+ ACSF (thin line) and during application of glycine (Left; thick line) or d-serine (Right; thick line) are superimposed. The application of glycine and d-serine did not change the amplitude of the NMDAR currents in GlyT1(+/-) pyramidal cells (B). (C) Histogram showing the effects of glycine (10 μM) and d-serine (10 μM) on NMDAR currents as percentage increase of the control. *, Difference was significant after to the application of glycine (open bar) and d-serine (filled bar) on WT mouse pyramidal cells (P < 0.005).