Figure 2.
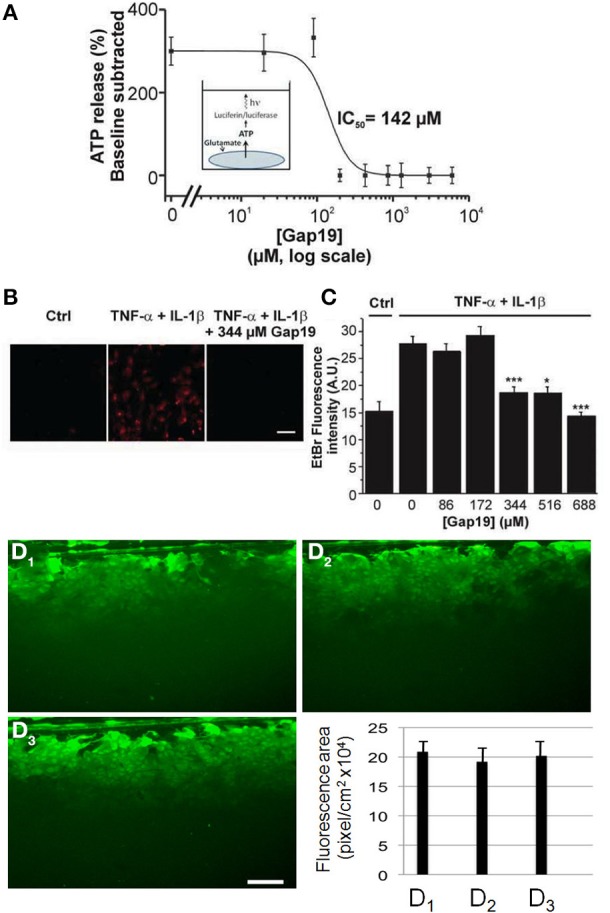
Dose-dependent inhibition of ATP release and Etd+ uptake through Cx43 hemichannels by Gap19 with lack of effect on gap junctional communication in cultured astrocytes. (A) Concentration-dependent inhibition by Gap19 (30 min pre-incubation) of ATP release in cultured cortical astrocytes triggered by glutamate (100 μM, 15 min application) (n = 6 independent experiments). (B) Representative images showing Etd+ uptake (red) in cultured astrocytes under control conditions (Ctrl) and after TNF-α/IL-1β or TNF-α/IL-1β + Gap19 treatment. Scale bar: 20 μm. (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001). (C) Summary data of Etd+ uptake studies in astrocytes, demonstrating inhibition by Gap19 (n = 5–8 independent experiments). Statistical comparisons refer to the stimulus condition without Gap19 (zero Gap19 concentration). (D1–D3) Representative images of scrape-loading dye transfer experiment in confluent cultures of astrocytes. Compared to control condition (D1), with Gap19 344 μM (D2, 30 min pre-incubation) or 688 μM (D3, 30 min pre-incubation). Lower graph: Quantification of scrape-loading data indicating that Gap19 did not influence gap junctional coupling as measured in confluent cultures of astrocytes (from left to right, bars are from control and the two tested concentrations of Gap19, respectively). (n = 3–5 independent experiments).
