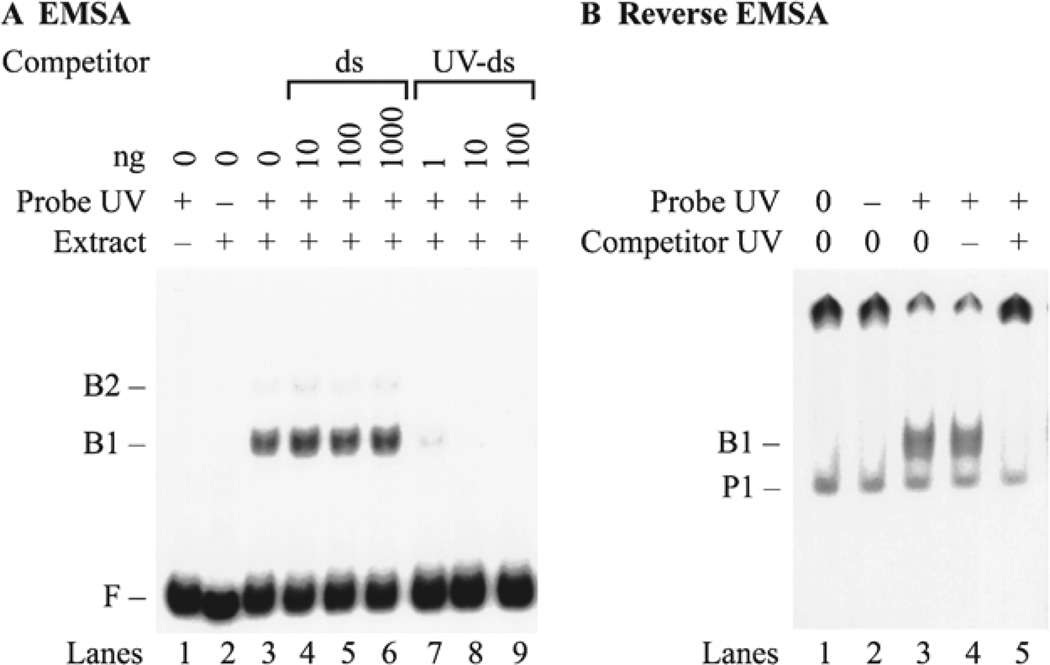
Fig. 2.
EMSA and reverse EMSA for UV-DDB. (a) EMSA. Crude protein extracts from HeLa cells were incubated with f148 probe DNA in the presence of different amounts of unlabeled competitor DNA. The probe DNA was UV irradiated (lanes 1 and 3–9) or left intact (lane 2). Protein extract was omitted (lane 1) or added (lanes 2–9). Control binding reactions omitted competitor DNA (lanes 1–3). Competition was carried out with intact double-stranded DNA (ds) (lanes 4–6), UV-irradiated double-stranded DNA (UV-ds) (lanes 7–9). (b) Reverse EMSA. The fraction of 35S-labeled DDB1 protein that bound to a UV-DNA cellulose column was assayed in a binding reaction with unlabeled f148 DNA. Probe DNA was omitted (lane 1), added as undamaged DNA (lane 2), or added as UV-damaged DNA (lanes 3 – 5). Unlabeled plasmid competitor DNA was either omitted (lanes 1–3), added as undamaged DNA (lane 4), or added as UV-damaged DNA (lane 5). Some of the 35S-labeled DDB1 protein is retained in the well of the gel (P2) because it was purified from a UV-DNA cellulose column, so that some high molecular weight UV-damaged DNA co-eluted as a complex with 35S-labeled DDB1 protein.