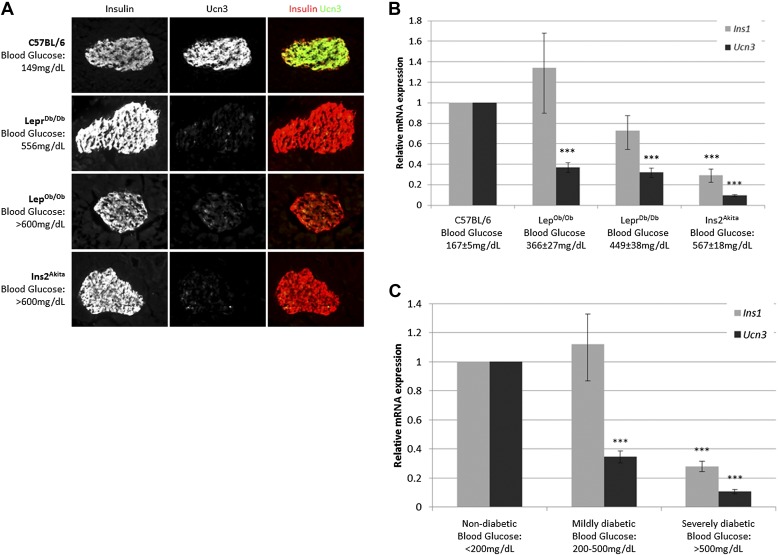
Figure 1. Loss of Ucn3 expression is an early marker for β cell de-differentiation in diabetes.
(A) Immunostaining with antibodies against insulin (red) and Ucn3 (green) in pancreata from T2D (LepOb/Ob and LeprDb/Db), insulin-dependent diabetic (Ins2Akita), and healthy control (C57BL/6) mice. Ucn3 protein but not insulin protein is down regulated in diabetic pancreata compared to the healthy control. (B) Quantitative Real-Time PCR analysis of Ins1 and Ucn3 gene expression in islets from C57BL/6 (n = 10), LepOb/Ob (n = 9), LeprDb/Db (n = 8), and Ins2Akita (n = 11) mice. Ucn3 mRNA is significantly reduced in all diabetes models, while insulin mRNA is significantly reduced only in the most diabetic model (Ins2Akita). (C) Quantitative Real-Time PCR analysis of Ins1 and Ucn3 gene expression in islets from non-diabetic control mice (n = 10; average blood glucose 167 ± 5 mg/dl), mildly diabetic (n = 16; average blood glucose 381 ± 17 mg/dl) and severely diabetic mice (n = 11; average blood glucose 588 ± 8 mg/dl). Error bars represent ±SEM. ***p < 0.001.