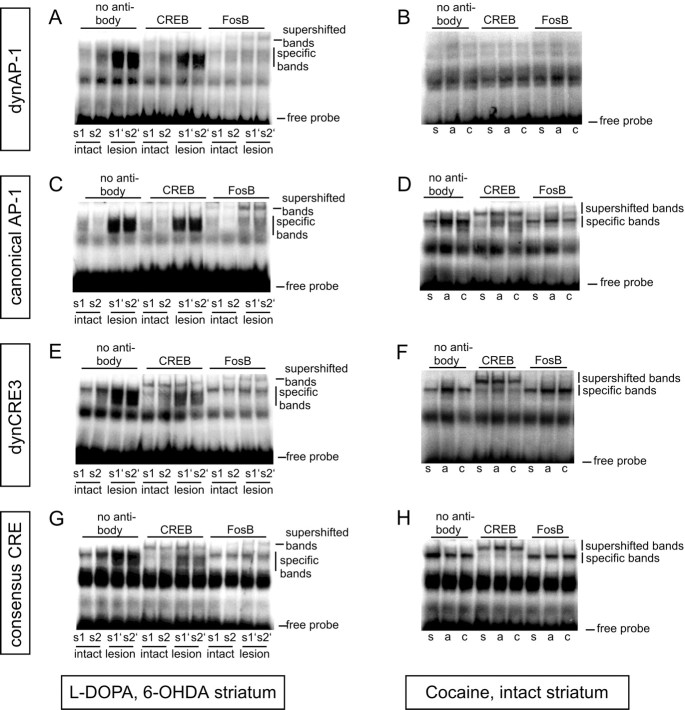
Fig. 9.
FosB/ΔFosB-related proteins are the predominant transcription factors bound to CRE and AP-1 enhancers inl-DOPA-treated rats. To study the contribution of CREB- or FosB/ΔFosB-related proteins to the DNA binding activity induced byl-DOPA (A, C,E, G) or cocaine (B,D, F, H), supershift assays were performed using antisera against CREB or FosB/ΔFosB. Antibodies were preincubated with striatal protein extracts before addition of the radioactively labeled promoter elements dynAP-1 (A, B), canonical AP-1 (C, D), dynCRE3 (E,F), and consensus CRE (G,H). The experiments were repeated at least three times with samples from different rats. In the left-hand pictures, s1 and s2 are protein extracts from intact striata of two chronicallyl-DOPA-treated rats, whereas s1′ ands2′ are extracts from the corresponding 6-OHDA-lesioned side. Rats treated with acute l-DOPA showed comparable results. In the right-hand pictures, s,a, and c are protein extracts from animals treated with saline, acute cocaine, or chronic cocaine, respectively.