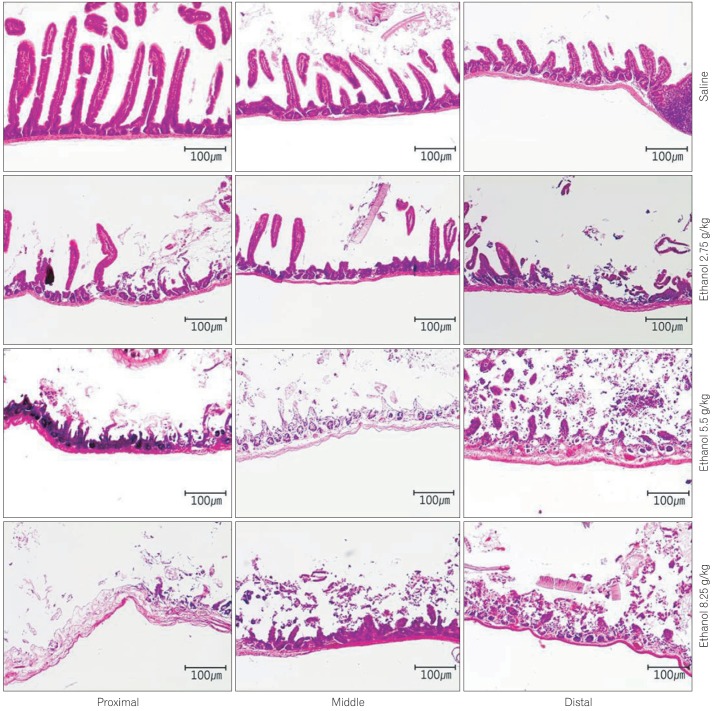
Fig. 1.
Pathology of the small intestinal mucosa and muscle induced by treatment with saline or ethanol (2.75 g/kg, 5.5 g/kg, 8.25 g/kg) (H&E, ×100). In saline-treated mice, villi were intact and normal lymphoid follicles were observed without infiltration of inflammatory cells. In mice treated with 2.75 g/kg of ethanol, focal falling off of villi and an edematous glandular layer were observed. These changes were more severe in the distal part with villi damage. In the group treated with 5.5 g/kg of ethanol, mulfifocal villi elimination, glandular layer destruction, erosions, and ulcers were observed with a severe aspect in the distal part. In mice treated with 8.25 g/kg of ethanol, diffuse damage extended to serosa, severe ulcers, and irregular expansion of lumen due to ischemic changes.