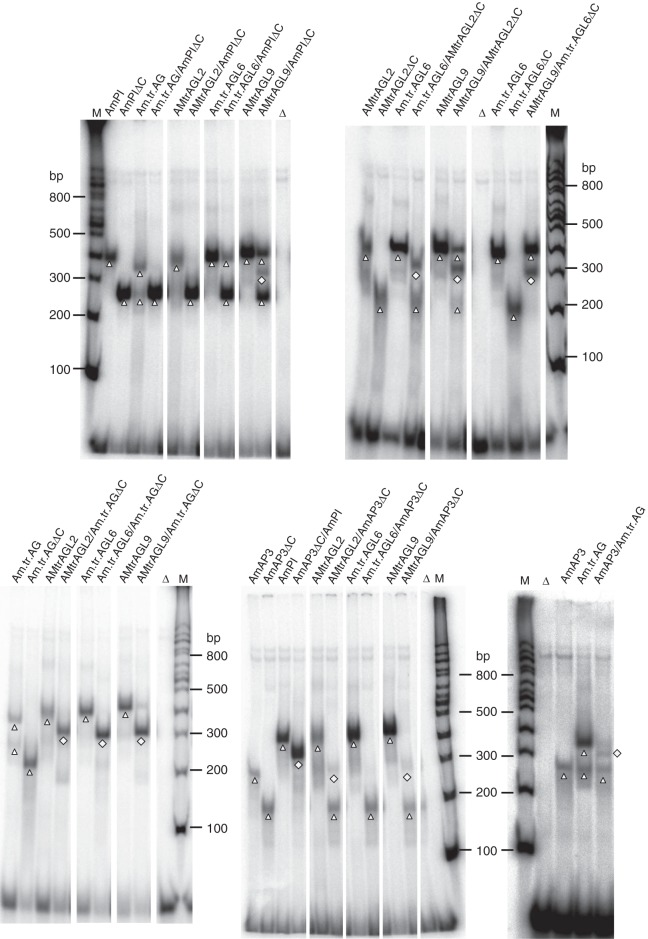
Fig. 3.
EMSA results for MADS-domain proteins from A. trichopoda. In vitro translated proteins were incubated together with a radioactively labelled DNA probe which carried one CArG-box. Proteins applied are noted above the gel. ‘ΔC’ is used to indicate C-terminal deleted proteins. Triangles highlight homomeric DNA-bound complexes; squares highlight heteromeric DNA-bound complexes. Free DNA is seen at the bottom of the gels. Homomeric complexes were not always visible when heteromer formation was tested, possibly because the vast majority of protein was assembled into DNA-bound heteromeric complexes (AmAP3ΔC/AmPI, for example) or in heteromeric complexes not or only very weakly binding to DNA (AMtrAGL9/AmAP3ΔC, for example). Note that certain potential heteromeric complexes were very weak and sometimes difficult to distinguish from homomeric complexes (AMtrAGL2/AmAP3ΔC, for example). For unknown reasons, the homomeric AmAP3–DNA complex possessed an unsusually high electrophoretic mobility and some proteins (Am.tr.AG, for example) formed two distinct protein–DNA complexes even in the absence of a partner. ‘Δ’ indicates negative controls in which in vitro translation lysate programmed with a vector that did not contain a cDNA insert was added. ‘M’ denotes lanes in which a radioactively labelled DNA marker (NEB 100 bp DNA ladder) was applied (bp = base pairs).