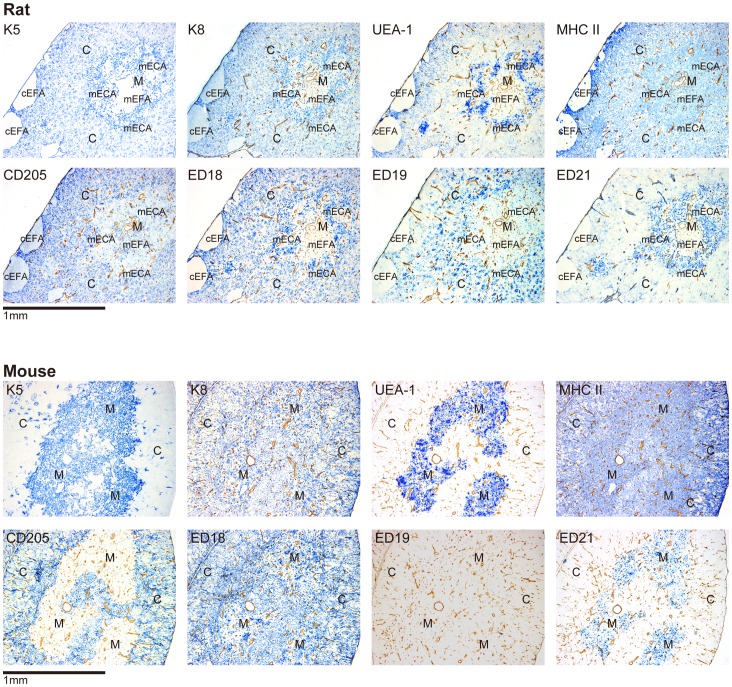
Figure 1. Immunohistological analysis of thymic epithelial cell-associated molecules in the thymi of rats and mice.
Double immunoenzyme staining for molecules of interests (blue) and tissue frameworks (type IV collagen, brown) Cortical (subcapsular) and medullary epithelium-free areas unique to rats are indicated by “cEFA” and “mEFA”, respectively. Epithelium-containing areas in the medulla are indicated by “mECA”. The antibodies used were anti-K5 followed by anti-rabbit IgG, anti-K8 followed by anti-chicken IgY, and anti-mouse CD205 followed by anti-rat IgG. Anti-rat MHCII and anti-rat CD205 followed by biotin-conjugated anti-mouse IgG, and biotin-conjugated anti-mouse MHCII, and biotin-conjugated ED18/ED19/ED21 were further reacted with anti-biotin antibody. Secondary antibodies and anti-biotin antibody were all conjugated with alkaline phosphatase and developed with the Vector Blue substrate kit. Tissue frameworks were stained with anti-type IV collagen antibody followed by peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG and developed with 3, 3′-diaminobenzidine substrate.