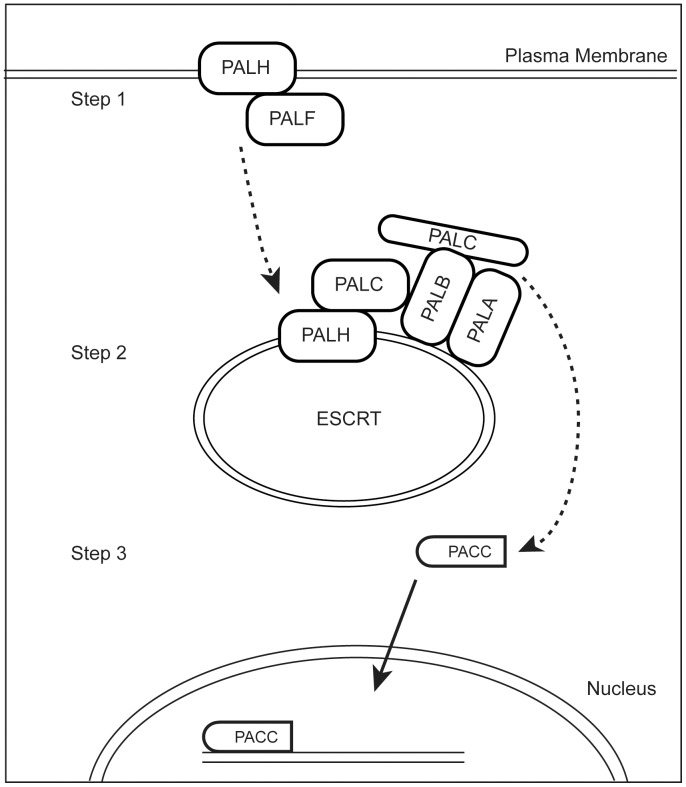
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the N. crassa PACC pathway.
The PACC signal transduction pathway elements found in N. crassa, and the model for how the pathway might function are depicted. The PALH and PALF proteins are thought to be found at the plasma membrane. PALH is a seven transmembrane receptor which is sensitive to environmental cues. PALF is an arrestin type protein that associates with PALH. PALF is phosphorylated and ubiquitinated in response to the environmental cues. These events lead to the endocytosis of the PALH/PALF complex. Following endocytosis, the PALH is directed into an ESCRT compartment, where it enters into a signaling complex containing PALA, PALB, PALC, and PACC. Within the signaling complex, PALB functions as a protease which cleaves PACC. This cleavage event removes a C-terminal inhibitory domain from the PACC transcription factor, and the processed PACC is released from the signaling complex. The activated PACC then enters the nucleus and directs transcriptional activity leading to the formation of the protoperithecium.